[Survey] HPCforML and MLforHPC
- HPCforML and MLforHPC Survey
- HPC and Big Data
- HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part A: Outline, Data on the Evolution of Interests and Communities
- HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part B: More on the Evolution of Interests and Communities
- HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part C: MLaroundHPDC/HPC and MLAutotuning
- HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part D: Learning Model Details and Agent Based Simulations
- HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part E: Challenges and Opportunities, Conclusions
- Understanding ML driven HPC: Applications and Infrastructure
- Learning Everywhere: A Taxonomy for the Integration of Machine Learning and Simulations
- ML for HPC and HPC for AI Workflows: The Differences, Gaps and Opportunities with Data Management
- Intelligent Data Center Architecture to Enable Next Generation HPC AI Platforms
- Deep Learning on HPC: Performance Factors and Lessons Learned
- HPC and Big Data
HPCforML and MLforHPC Survey
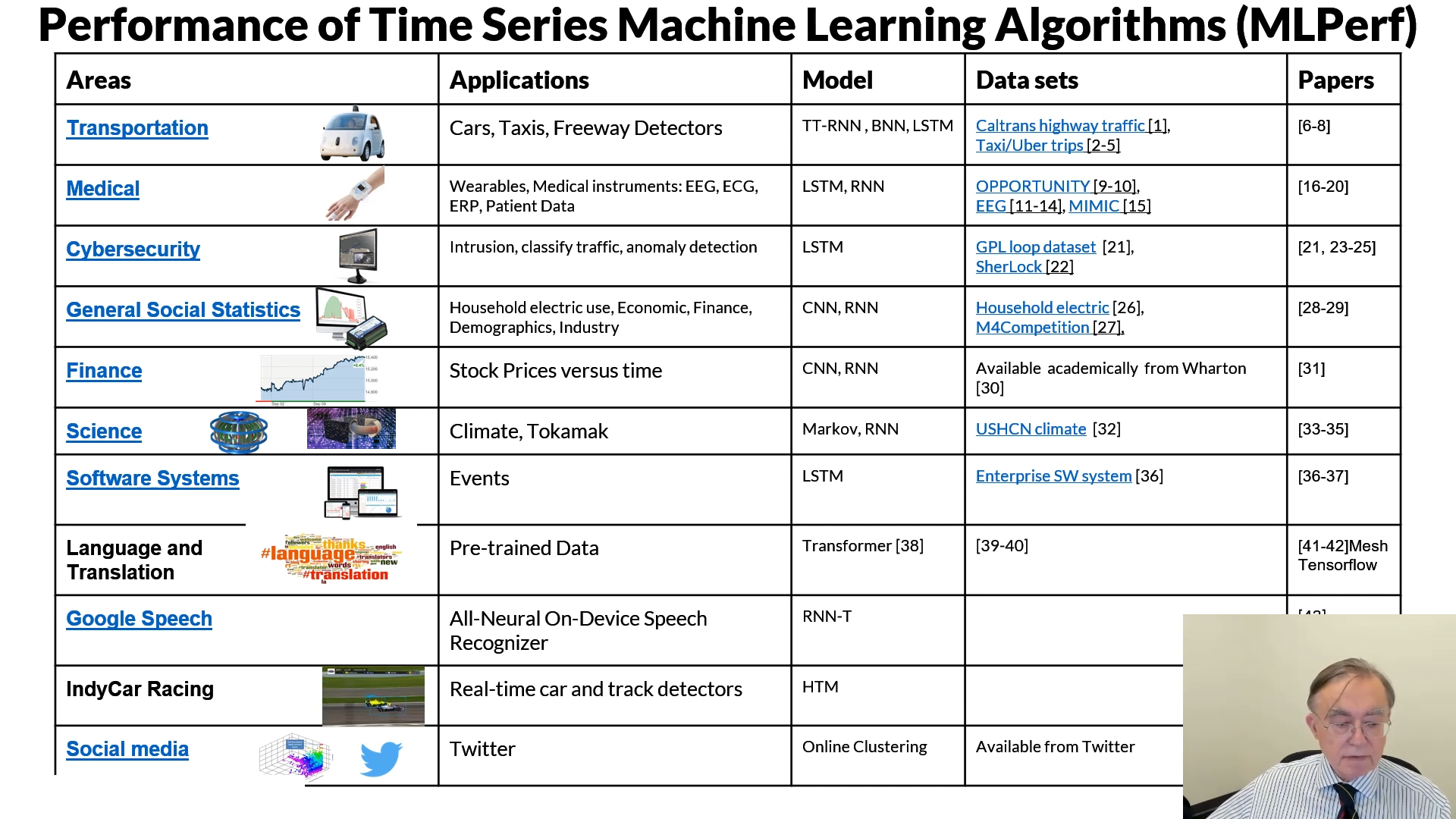
Due to the possibility of the population of MLforHPC and the next generation hybrid components architectures, we began the survey of HPCforML and MLforHPC, but I'd like to call it as SystemforML and MLforSystem, then we can use this kind of terms as a guidance to design our hybrid architectures not only in HPC but also other levels.
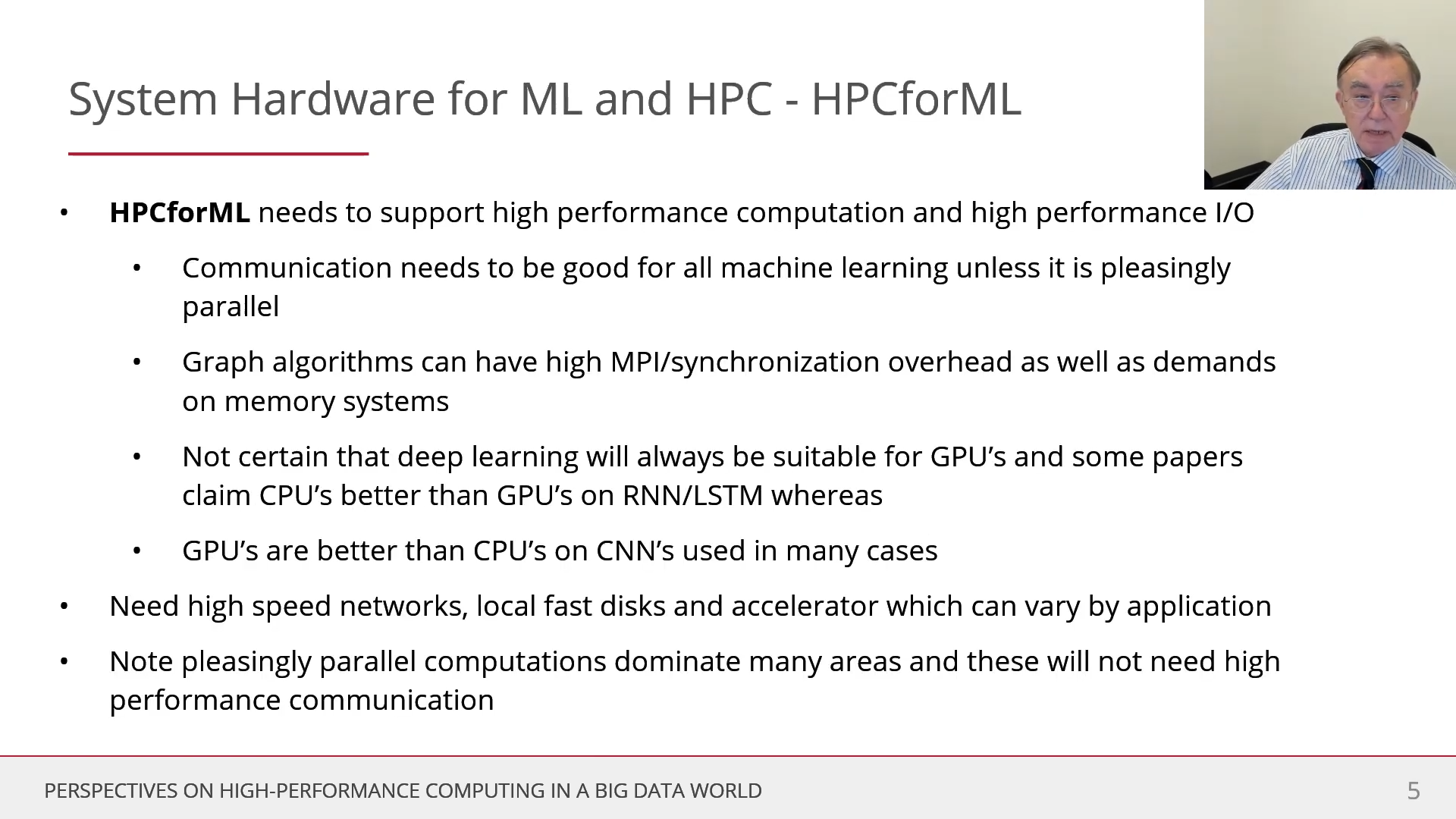
HPCforML, or SystemforML, uses HPC to execute and enhance ML performance, or using HPC simulations to train ML algorithms (theory guided machine learning), which are then used to understand experimental data or simulations.
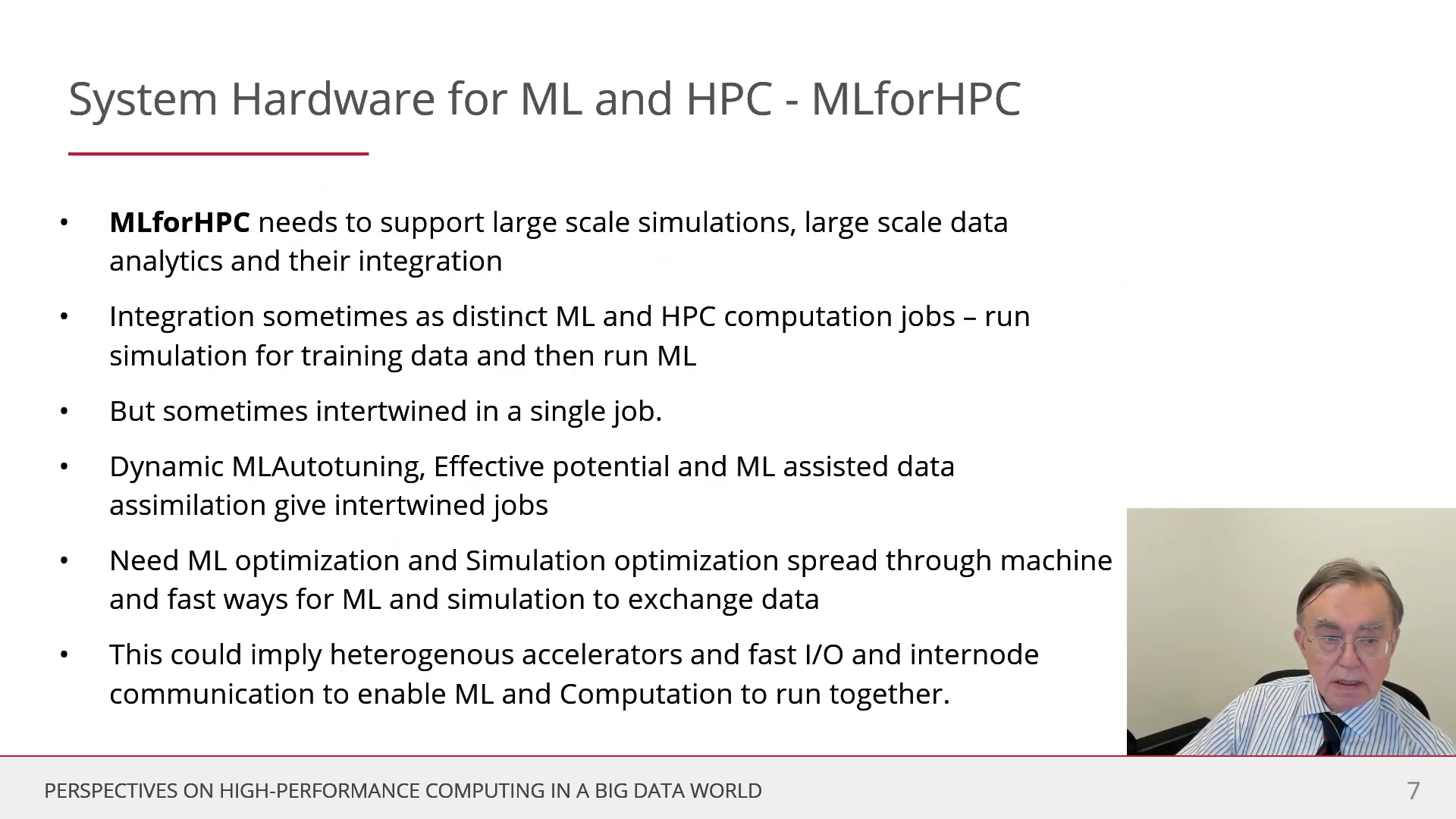
MLforHPC, or MLforSystem, uses ML to enhance HPC applications and systems, where big data comes from the computation and/or experimental sources that are coupled to ML and/or HPC elements. MLforHPC can be further subdivided as MLaroundHPC, MLControl, MLAutotuningHPC, and MLafterHPC.
HPC and Big Data
HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part A: Outline, Data on the Evolution of Interests and Communities
HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part B: More on the Evolution of Interests and Communities



HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part C: MLaroundHPDC/HPC and MLAutotuning
MLAutotuning and MLaroundHPC

HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part D: Learning Model Details and Agent Based Simulations
HPC and Big Data (Long) – Part E: Challenges and Opportunities, Conclusions



Understanding ML driven HPC: Applications and Infrastructure
HPCforML
HPCforML uses HPC to execute and enhance ML performance, or using HPC simulations to train ML algorithms (theory guided machine learning), which are then used to understand experimental data or simulations.
MLforHPC
MLforHPC uses ML to enhance HPC applications and systems, where big data comes from the computation and/or experimental sources that are coupled to ML and/or HPC elements. MLforHPC can be further subdivided as MLaroundHPC, MLControl, MLAutotuningHPC, and MLafterHPC.
MLaroundHPC
Using ML to learn from simulations and produce learned surrogates for the simulations. This increases effective performance for strong scaling where we keep the problem fixed but run it faster or run the simulation for a longer time interval such as that relevant for biological systems. It includes SimulationTrainedML where the simulations are performed to directly train an AI system rather than the AI system being added to learn a simulation.
MLaroundHPC: Learning Outputs from Inputs
Simulations performed to directly train an AI system, rather than AI system being added to learn a simulation.
MLaroundHPC: Learning Simulation Behavior
ML learns behavior replacing detailed computations by ML surrogates.
MLaroundHPC: Faster and Accurate PDE Solutions
ML accelerated algorithms approximate the solution high dimensional PDEs such as the diffusion equation using a Deep Galerkin Method (DGM), and train their network on batches of randomly sampled time and space points.
MLaroundHPC: New Approach to Multi-Scale Modeling
Machine learning is ideally suited for defining effective potentials and order parameter dynamics, and shows significant promise to deliver orders of magnitude performance increases over traditional coarse-graining and order parameter approaches. See well established methods.
MLControl
Experiment Control
Using simulations (possibly with HPC) in control of experiments and in objective driven computational campaigns.
Experiment Design
Model-based design of experiments (MBDOE) with new ML assistance [24] identifies the optimal conditions for stimuli and measurements that yield the most information about the system given practical limitations on realistic experiments.
MLAutoTuning
MLAutoTuning can be applied at multiple distinct points, and can be used for a range of tuning and optimization objectives. For example:
- mix of performance and quality of results using parameters provided by learning network [4], [25]–[28];
- choose the best set of “computation defining parameters” to achieve some goal such as providing the most efficient training set with defining parameters spread well over the relevant phase space [29], [30];
- tuning model parameters to optimize model outputs to available empirical data [31]–[34].
MLafterHPC
ML analyzing results of HPC as in trajectory analysis and structure identification in biomolecular simulations.
Learning Everywhere: A Taxonomy for the Integration of Machine Learning and Simulations
HPCforML
HPCrunsML
Using HPC to execute ML with high performance.
SimulationTrainedML
Using HPC simulations to train ML algorithms, which are then used to understand experimental data or simulations.
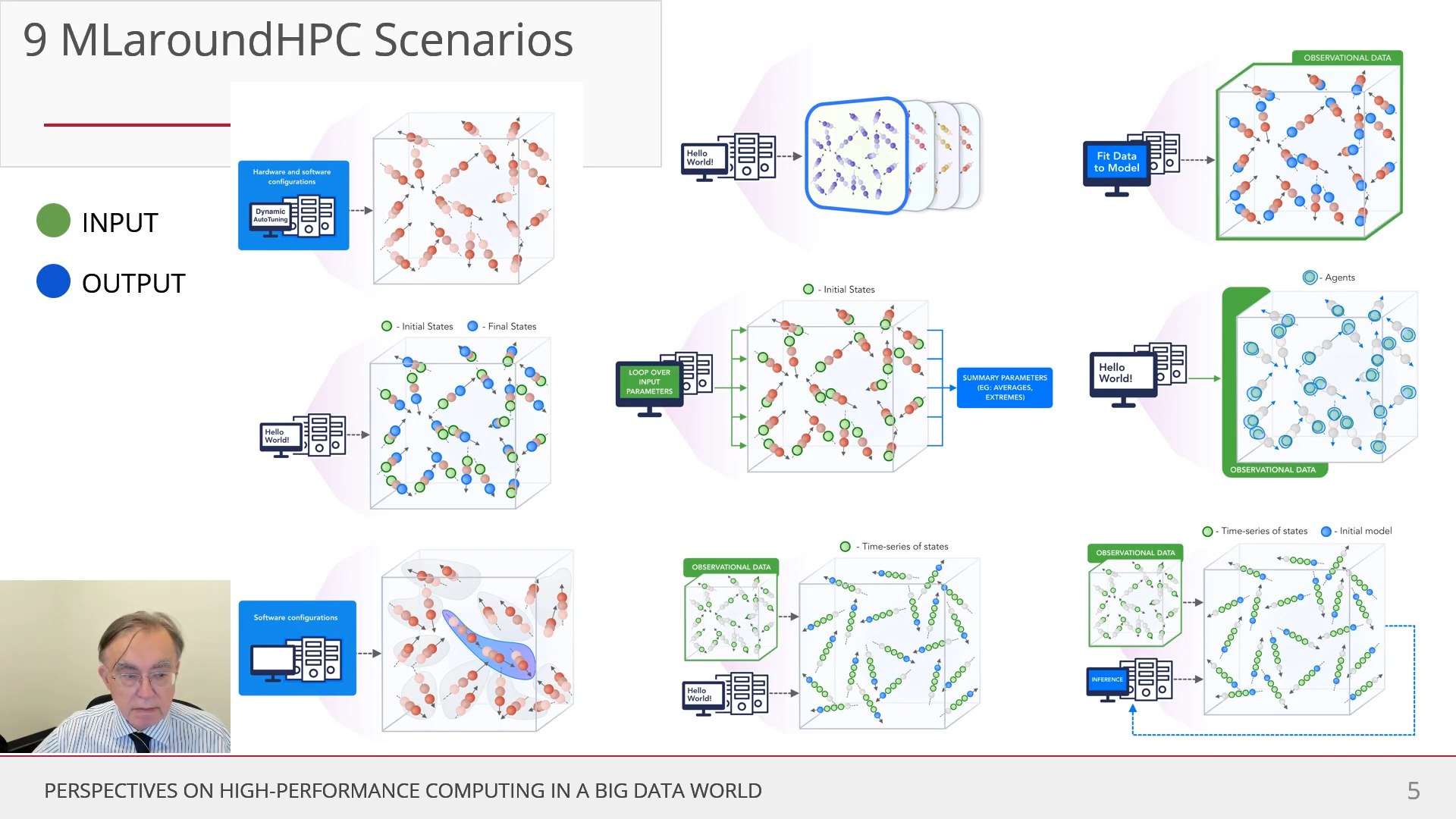
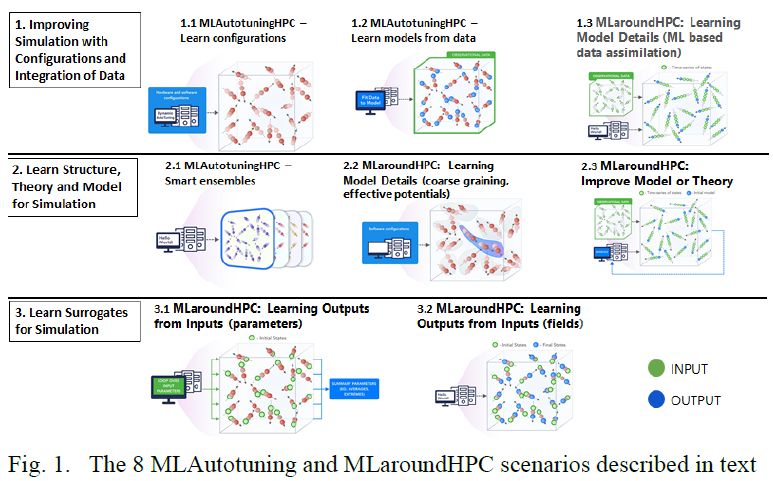
Taxonomy Of MLAutotuningHPC And MLaroundHPC: Improving Simulation With Configurations And Integration Of Data
MLAutotuningHPC: Learn configurations
Figure 2 illustrates this category, which is classic MLAutotuningHPC and one optimizes some mix of performance and quality of results with the learning network inputting the configuration parameters of the computation.
The configuration includes:
- initial values
- dynamic choices such as block sizes for cache use, variable step sizes in space and time.
This category can also include discrete choices as to the type of solver to be used.
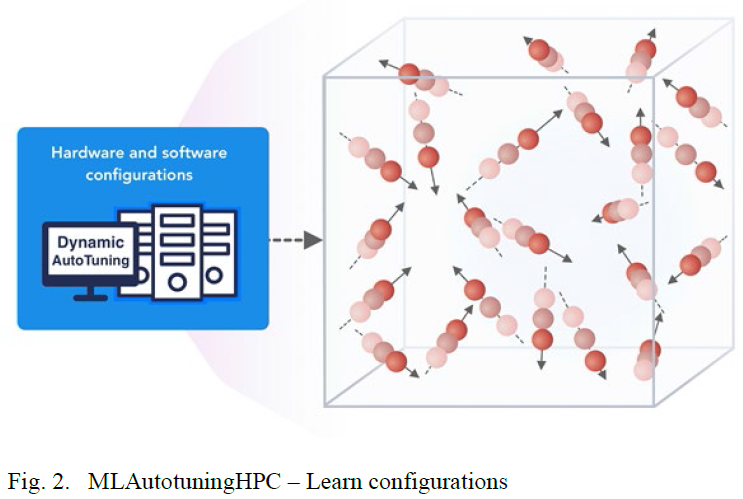
- Particle Dynamics-MLAutotuningHPC – Learn configurations
MLAutotuningHPC: Learning Model Setups from Observational Data
This category is seen when a simulation set up as a set of agents, perhaps each representing a cell in a virtual tissue simulation. One can use ML to learn the dynamics of cells replacing detailed computations by ML surrogates.
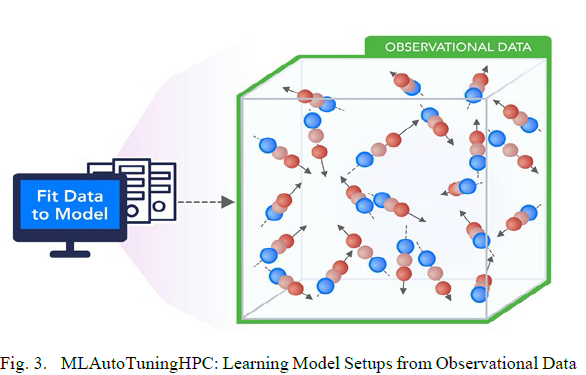
- Particle Dynamics-MLAutotuningHPC – Learning Model Setups from Observational Data
- ABM-MLAutotuningHPC – Learning Model Setups from Observational Data
- PDE-MLAutotuningHPC – Learning Model Setups from Observational Data
MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details - ML for Data Assimilation (predictor-corrector approach)
Data assimilation involves continuous integration of time dependent simulations with observations to correct the model with a suitable combined data plus simulation model. This is for example common practice in weather prediction field. Such current state of the art expresses the spatial structure as a convolutional neural net and the time dependence as recurrent neural net (LSTM).
Then as a function of time one iterates a predictor corrector approach, where one time steps models and at each step optimize the parameters to minimize divergence between simulation and ground truth data.
.png)
- ABM-MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details (ML based data assimilation)
- PDE-MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details (ML based data assimilation)
Taxonomy Of MLAutotuningHPC And MLaroundHPC: Learn Structure, Theory And Model For Simulation
MLAutotuningHPC: Smart ensembles
Here we choose the best strategy to achieve some computation goal such as providing the most efficient training set with defining parameters spread well over the relevant phase space. Ensembles are also essential in many computational studies such as weather forecasting or search for new drugs where regions of defining parameters need to be searched.
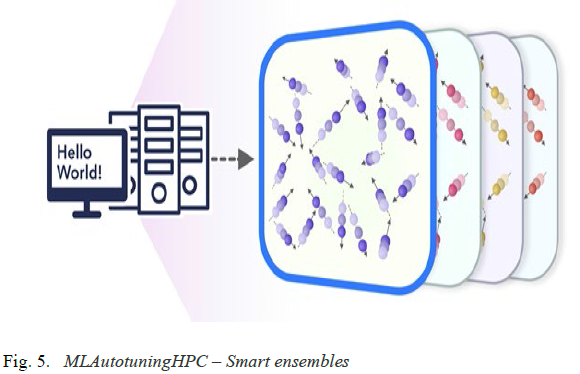
- General Simulations-MLAutotuningHPC – Smart ensembles
- Particle Dynamics-MLAutotuningHPC – Smart ensembles
- ABM-MLAutotuningHPC – Smart ensembles
MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details (effective potentials and coarse graining)
This is classic coarse graining strategy with recently, deep learning replacing dimension reduction techniques.) One can learn effective potentials and interaction graphs.
.png)
- Particle Dynamics-MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details (effective potentials)
- Particle Dynamics-MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details (coarse graining)
- PDE-MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details (coarse graining)
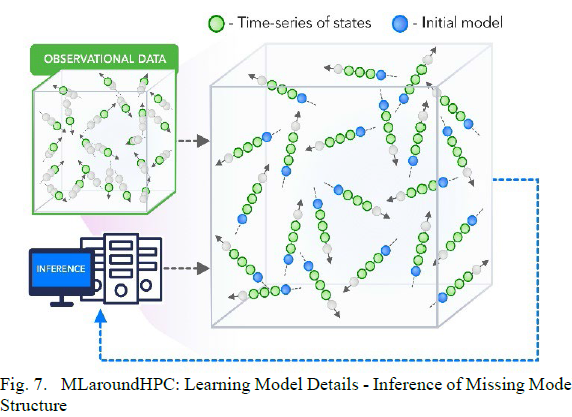
MLaroundHPC: Learning Model Details - Inference of Missing Model Structure
AI will essentially be able to derive theories from data, or more practically a mix of data and models. This is especially promising in agent based models which often contain phenomenological approaches such as the predictor-corrector method.
Taxonomy Of MLAutotuningHPC And MLaroundHPC: Learn Surrogates For Simulation
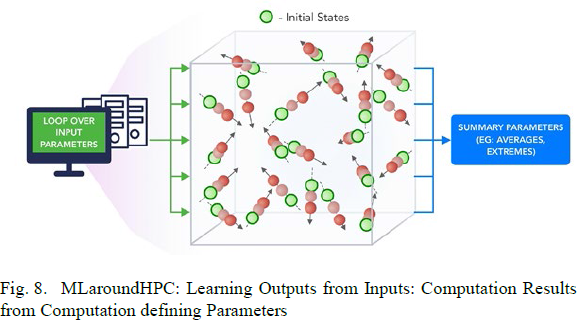
MLaroundHPC: Learning Outputs from Inputs: a) Computation Results from Computation defining Parameters
In this category, one just feeds in a modest number of meta-parameters that define the problem and learn a modest number of calculated answers.
Operationally this category is the same as SimulationTrainedML but with a different goal: In SimulationTrainedML the simulations are performed to directly train an AI system rather than the case here where the AI system is being added to learn a simulation.
- Particle Dynamics- MLaroundHPC: Learning Outputs from Inputs (parameters)
- PDE-MLaroundHPC - Learning Outputs from Inputs (parameters)
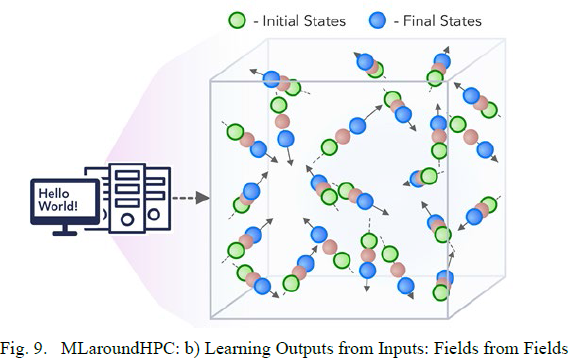
MLaroundHPC: Learning Outputs from Inputs: b) Fields from Fields
Here one feeds in initial conditions and the neural network learns the result where initial and final results are fields.
- Particle Dynamics-MLaroundHPC: Learning Outputs from Inputs (fields)
- ABM-MLaroundHPC: Learning Outputs from Inputs (fields)
- PDE-MLaroundHPC: Learning Outputs from Inputs (fields)
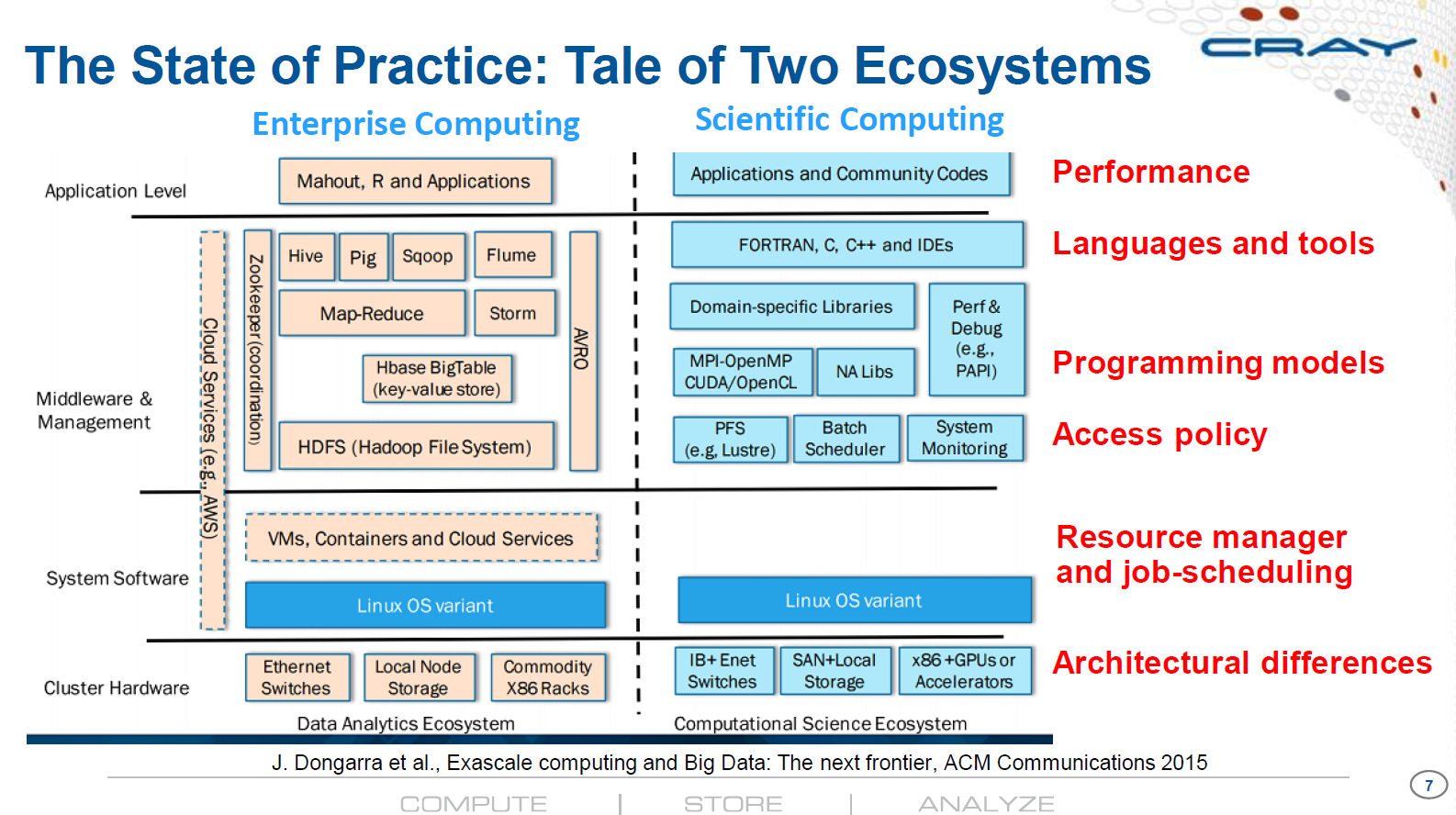
ML for HPC and HPC for AI Workflows: The Differences, Gaps and Opportunities with Data Management
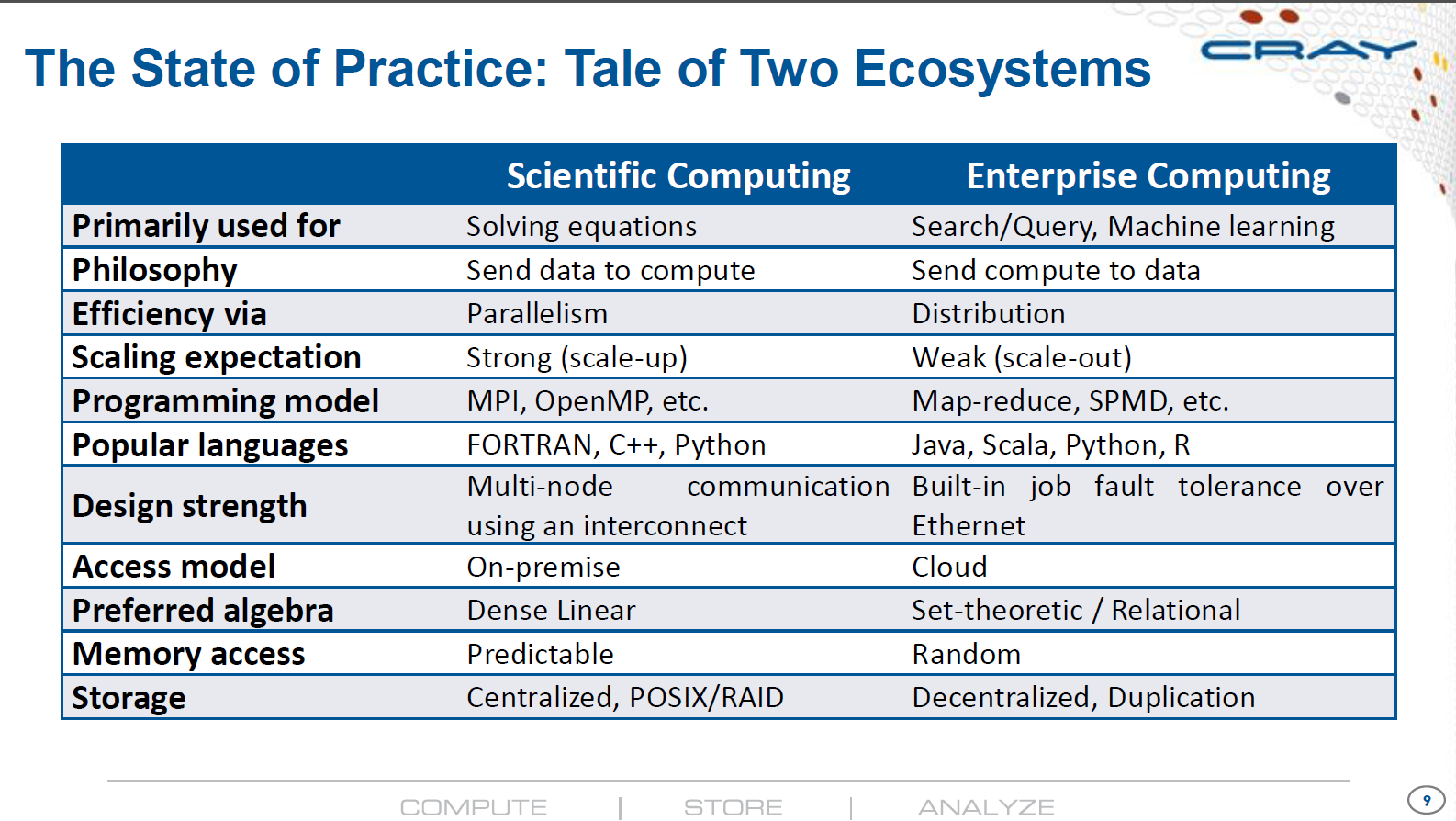
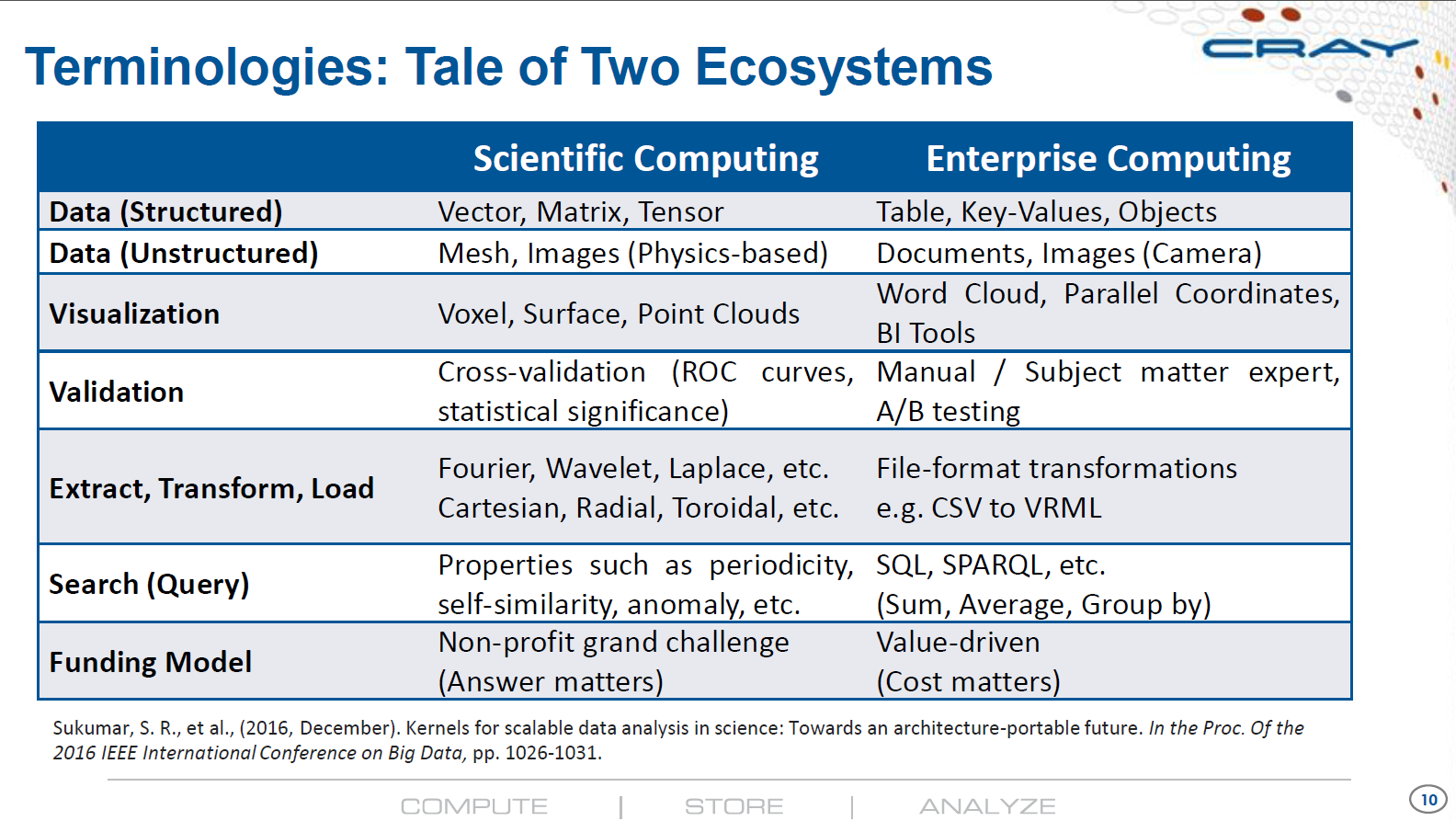
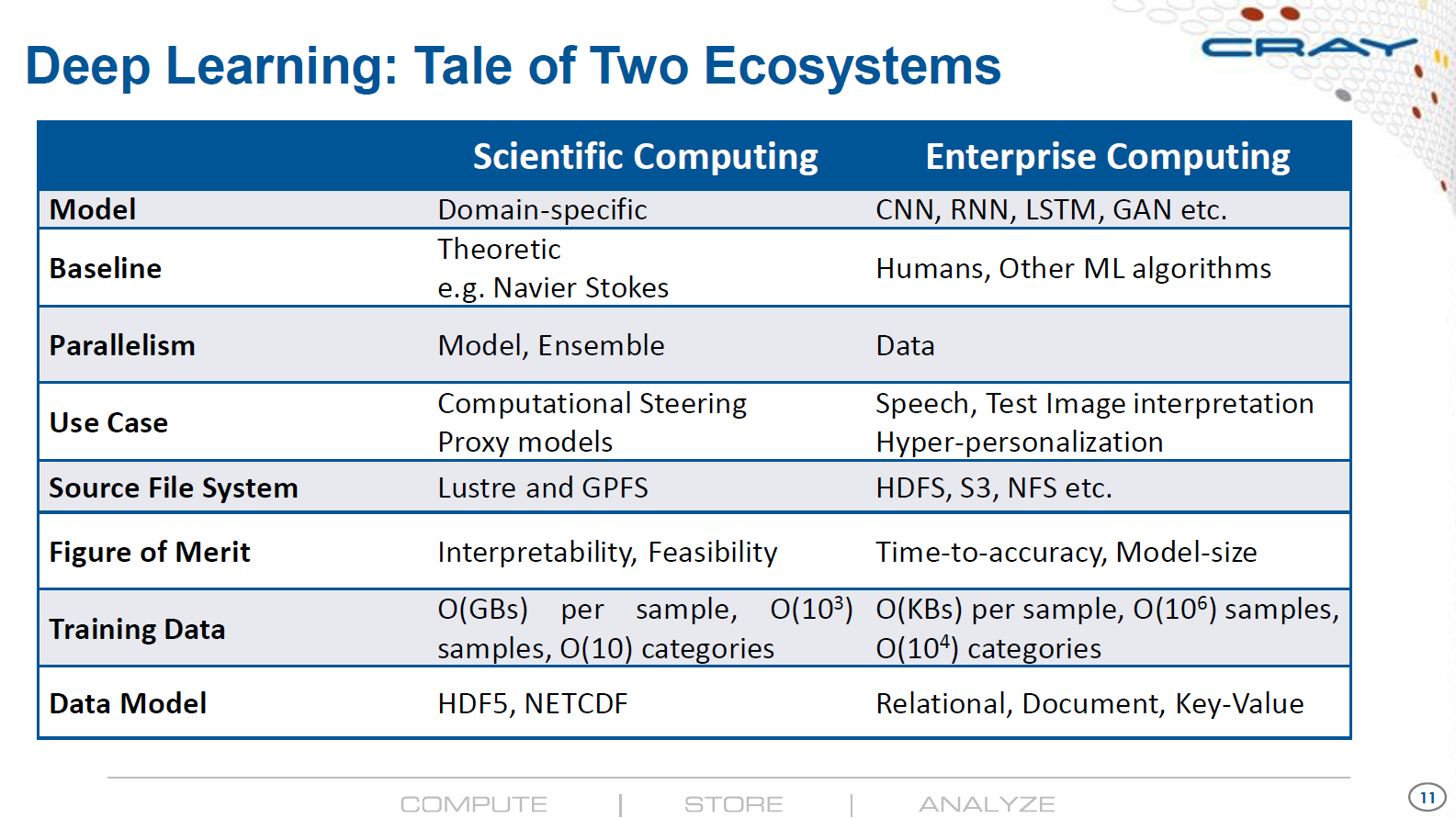
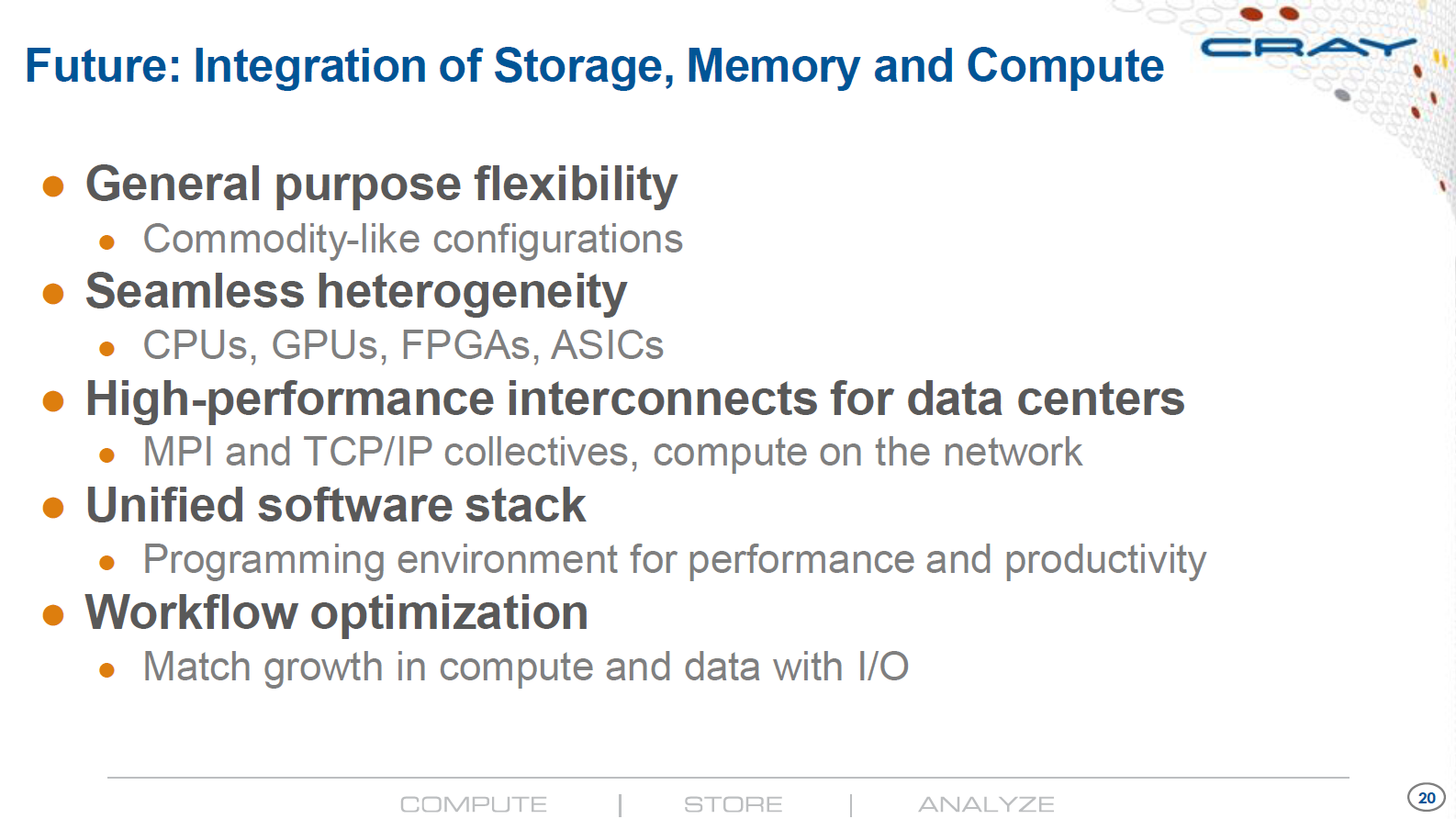
Intelligent Data Center Architecture to Enable Next Generation HPC AI Platforms
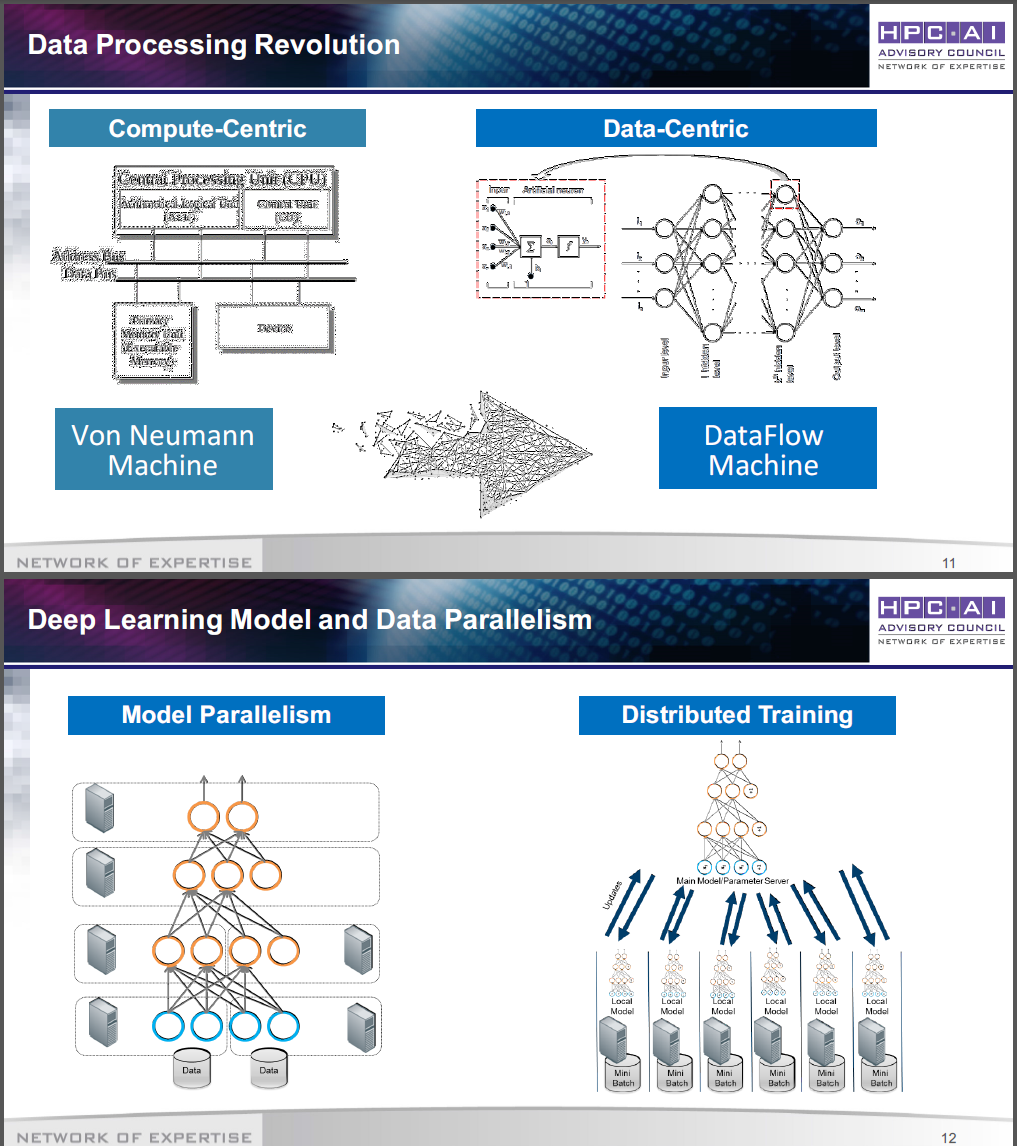

Deep Learning on HPC: Performance Factors and Lessons Learned
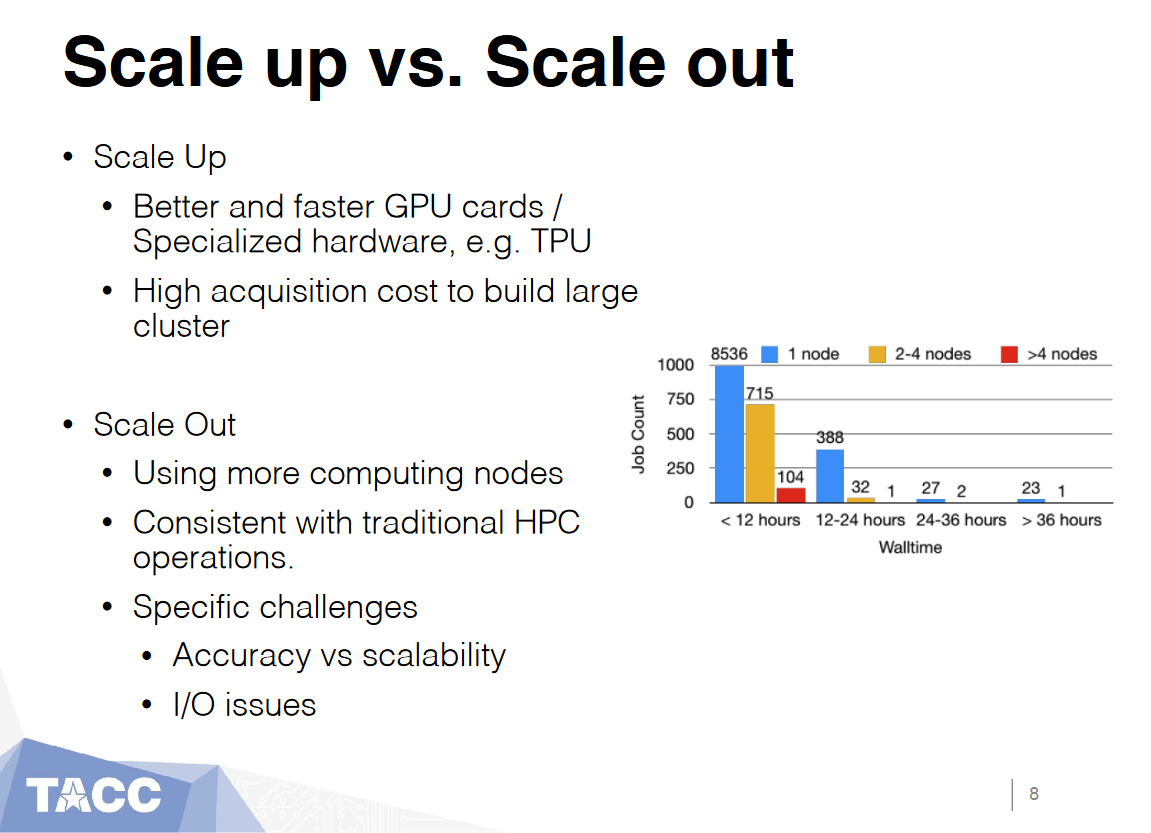
Scale up vs. Scale out
Conclusion

