[Emulate] Untimed TLM in SystemC
Untimed TLM in SystemC1
Untimed TLM – Data Flow Modeling
- Purposes
- Create initial draft of the specification model
- Focus
- Data flow and functionality modeling
- Kahn process network
- Deterministic, untimed model of computation
- How?
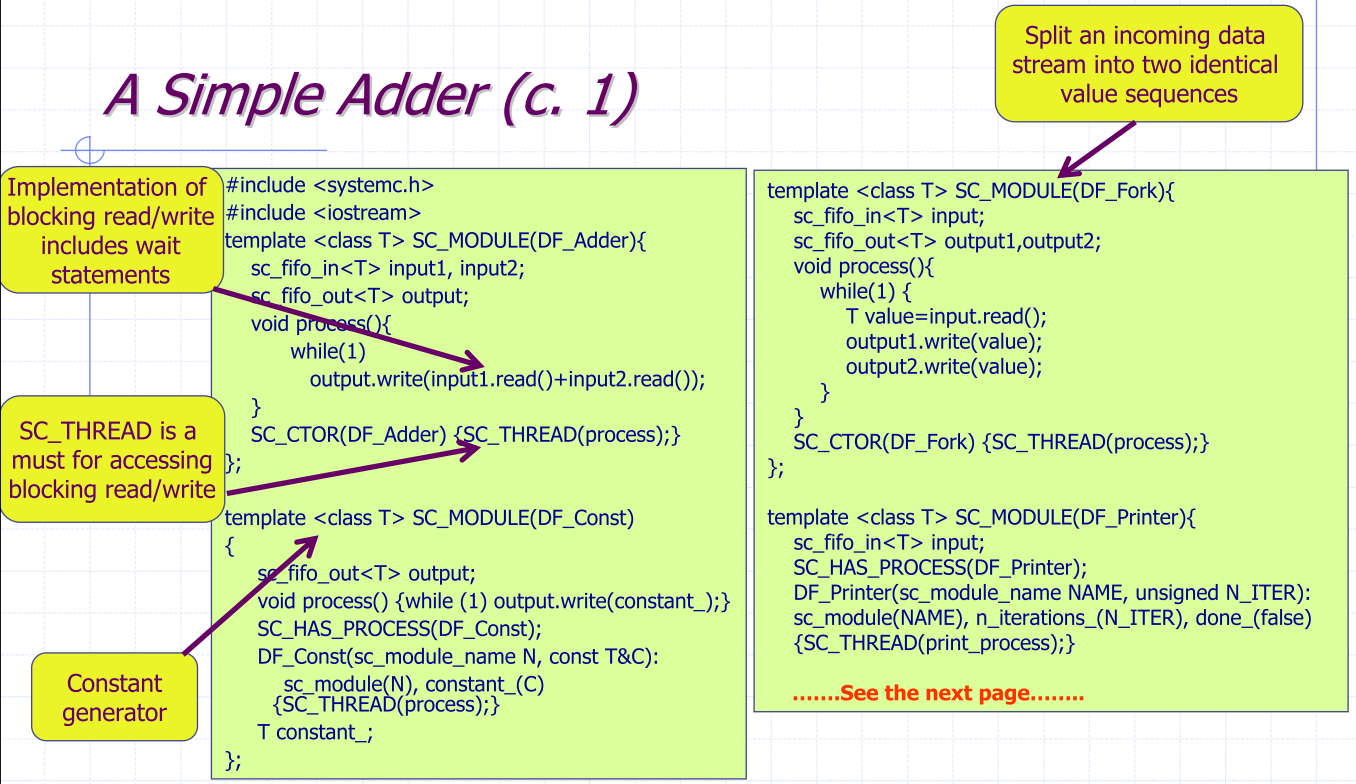
- Untimed processes are modeled with
SC_THREAD - Processes communicate through FIFO channels using blocking read/write
- Implicit system synchronization is achieved by the blocking read/write
- Blocking read is suspended until data is available in the FIFO channel
- Blocking write is suspended until more space is available in the FIFO channel
- Untimed processes are modeled with
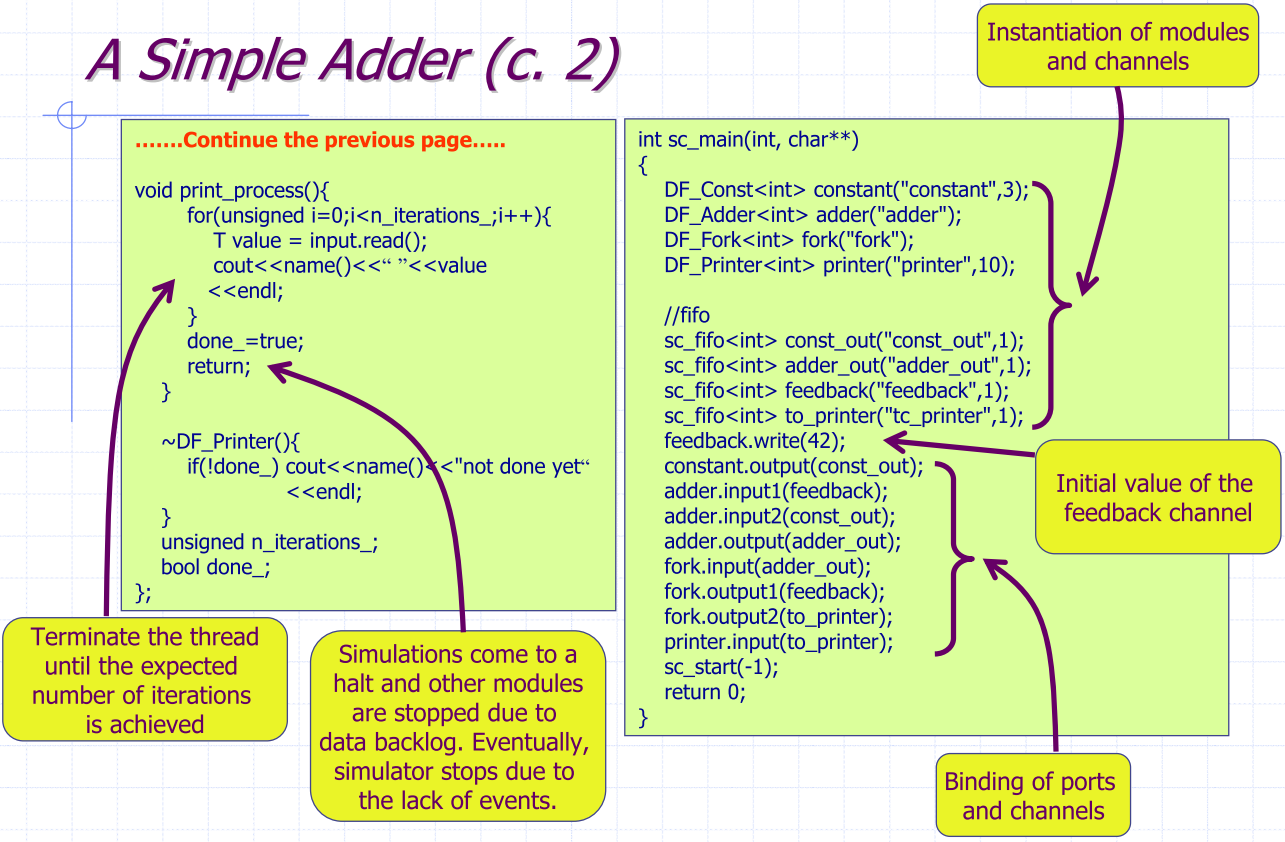
A Simple Adder
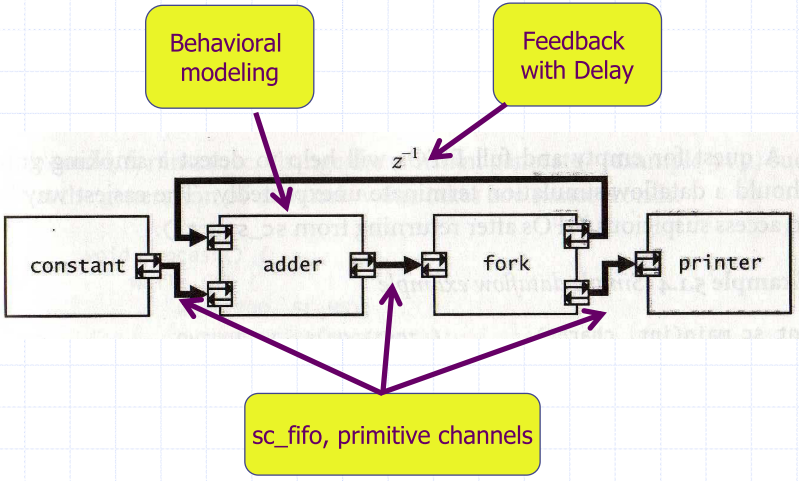
Dead Lock
- Missing initial values of the feedback channel
- The adder would never be able to read from its first input
- Unbalanced production and consumption rate in a feedback loop
- A producer and a consumer connected to a FIFO channel need to move the same number of tokens on the average
- If
DF_forkproduces two values on each output for every data sample consumed, the simulation would stall with the folk module attempting to write to its first output port
- A quest for empty and full FIFOs can help to identify the causes
- Access suspicious FIFOs after returning from
sc_start()
- Access suspicious FIFOs after returning from
FIFO Sizes
- FIFO sizes play a key role
- Determine whether a system deadlocks
- Have an impact on system behavior (value sequences)
- Have an impact on simulation speed
- Larger sizes cause less context switches and faster simulation
Insertion of Functional Delay
- Inserting functional delay in untimed TLM can be achieved by annotating the delay with
waitstatements SC_THREADis more preferable thanSC_METHOD- Adding delay information in method processes is nontrivial
- Maintaining blocking read/write semantics in method processes is next to impossible

Stopping Untimed TLM Simulation
- Simulation time will never advance in a purely untimed TLM
- Processes are simulated with advance of delta-cycles
- Using
sc_startwith a positive argument does not lead to the termination of the simulation
- How can one terminate the simulation?
- Solution I
- Use process termination and hope for data backlog
- Simulations are run until a sufficient amount of samples are obtained
- Example: the
print_processof theDF_printermodule
- It is not guaranteed to be successful
- The process may be in some dead branch of the system
- There could be multiple instances of
DF_printer- Logic and-combination of exit conditions is a must
- Use process termination and hope for data backlog
- Solution II
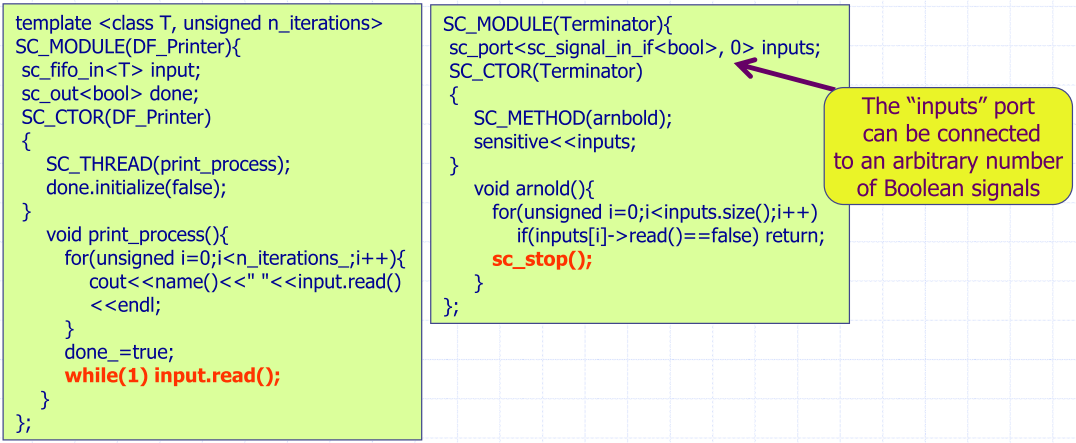
- Simply indicate the fact and continue to consume data
- Create a terminator module and monitor different exit conditions
- Combination of a given simulation time and data-dependent exit conditions can often be the best solution
- Solution I
-
IOC5080(5940) System Model Design and Verification, Department of Computer Science, National Chiao-Tung University ↩