[Emulate] Interface and Channel Design
Interface and Channel Design1
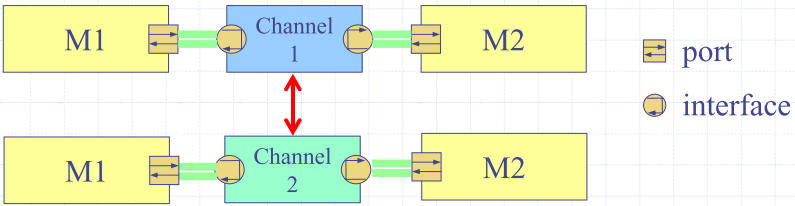
Interface and Channel
- Interfaces and channels provide a flexibly way to model communication and system synchronization
- Interface classes declare the access methods
- Channels implement the access methods declared within interfaces
- Interfaces separate the communication from the computation
- Communication refinement is achieved by allowing one channel to easily be swapped with another
Interface Design
- Good interface design shall reduce the modeling effort, make design refinement easier, and increase design reuse
- Guidelines for designing interface classes
- Minimize the number of distinctive interfaces
- Allow the channel implementation be easily swapped
- Leave the port instances untouched during the replacement of channels
- Layer specialized interfaces on more general interfaces
- Specialized interfaces inherit from generalized interfaces
- Use class inheritance to group common interface
- Create a common base class for different interface classes
- Use multiple inheritance to create a unified interface class
- Define the unified interface to inherit from separate interfaces without adding any new members
- Minimize the number of distinctive interfaces
Layered Interface Classes
Allow channel implement interfaces of different specialization.
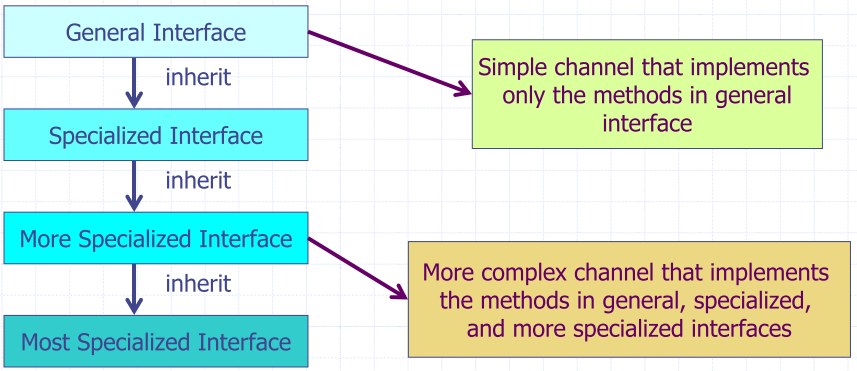
Channel Reuse
Modules use the least specialized interface, but channels that implement more-specialized interfaces can still be attached.
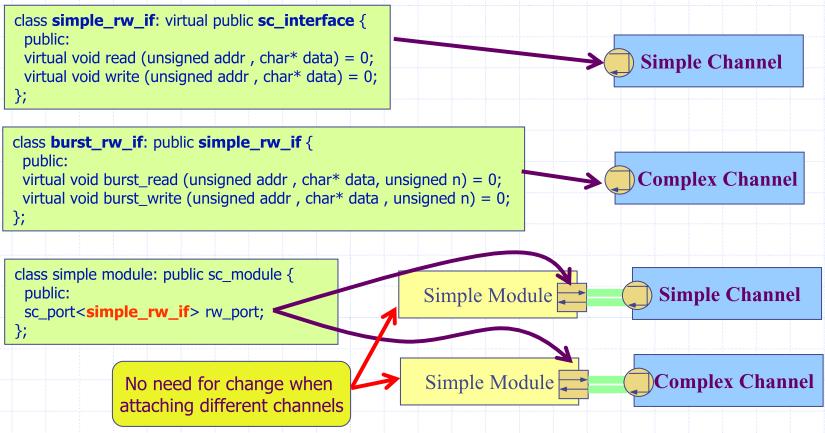
Channel Design
- Primitive channels
- Derived from
sc_prim_channel - Contain no hierarchy and processes
- May implement the request-update mechanism
- Faster simulation speed
- Derived from
- Hierarchical channels
- Derived from
sc_channel - May contain hierarchy and processes
- Slower simulation speed due to more processes and context switches
- Derived from
- What if your channel needs request-update mechanism and contains processes, ports, and modules?
- Split the channel into a primitive channel and a hierarchical channel
- Instance the primitive channel in the hierarchical one
Primitive Channels
Primitive Channels with Request-Update
- Key ideas of request-update
- Gather state change requests during the evaluation phase
- Determine the next state of the channel during the update phase
- Propagate the new channel state during the next delta-cycle
- Main uses
- Delta-cycle delay communication for hardware simulation
- A new value assigned to a channel does not take effect immediately
- There is always a delta-cycle delay before the new value takes effect
- Arbitration and resolution of simultaneous actions
- Simultaneous actions occur within the same simulation phase
- Either is free to execute before the other
- Example: multiple processes drive the same channel
- Delta-cycle delay communication for hardware simulation
- Primitive channels with request-update in SystemC
sc_fifo,sc_signal,sc_buffer,sc_signal_resolved,sc_signal_rv
Primitive Channels without Request-Update
sc_mutex
sc_mutex(mutual exclusion object)- Allow multiple processes share a common resource
- Usage
- The process using the resource locks the mutex and unlocks it afterwards when the resource is no longer needed
- Other processes must wait for the resource to be freed
- The process executing first after the unlock will succeed in locking the mutex
- There is no guarantee about which process will succeed
- Member functions
lock()- Lock the mutex (wait until unlocked if in use)
trylock()- Non-blocking, return true if success, else false
unlock()- Free previously locked mutex
sc_samphore
sc_samphore- Allow multiple processes share a set of common resources
- A generalized version of
sc_mutex
- Member functions
wait()- If available, occupy one semaphore
- Otherwise, suspend until there is an available resource
trywait()- If available, occupy one semaphore
- Otherwise, return -1
get_value()- Return number of available semaphore
post()- Free the previous occupied semaphore
Hierarchical Channels
- User defined channel
- May have embedded modules, channels, and processes
- Provide implementations for one or more interfaces
- A hierarchical channel is distinguished from a general module by the fact that it implements interfaces
- Used to encapsulate both the structural elements of a design and the communication protocol or methods
Channel Refinement
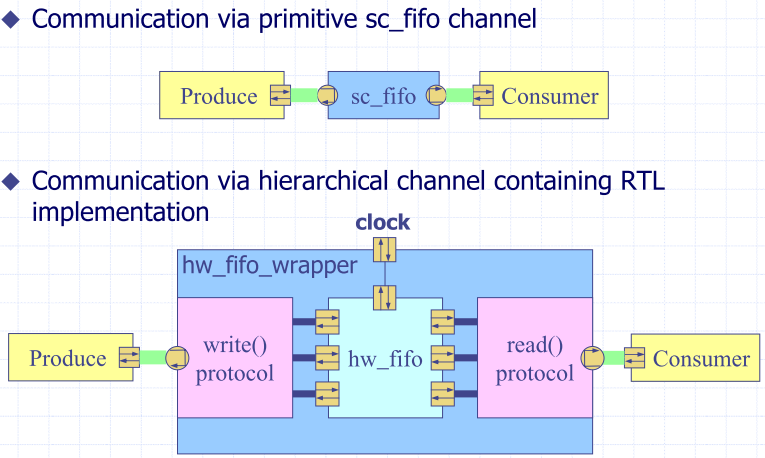
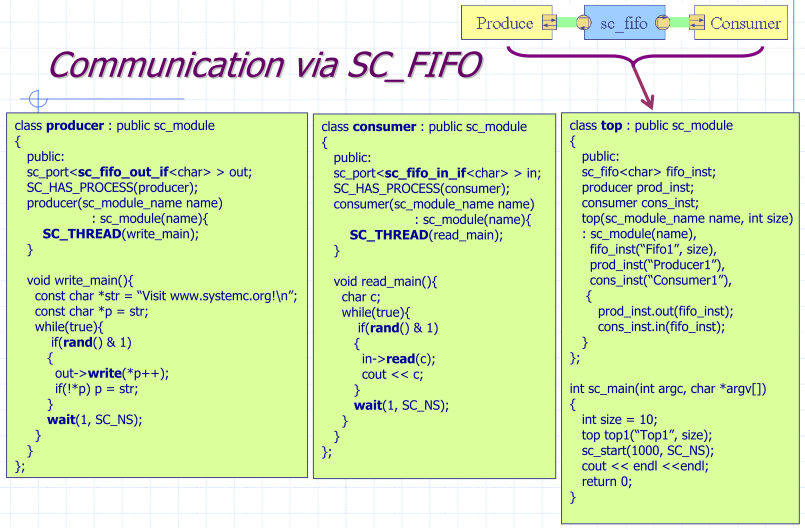
Communication via sc_fifo
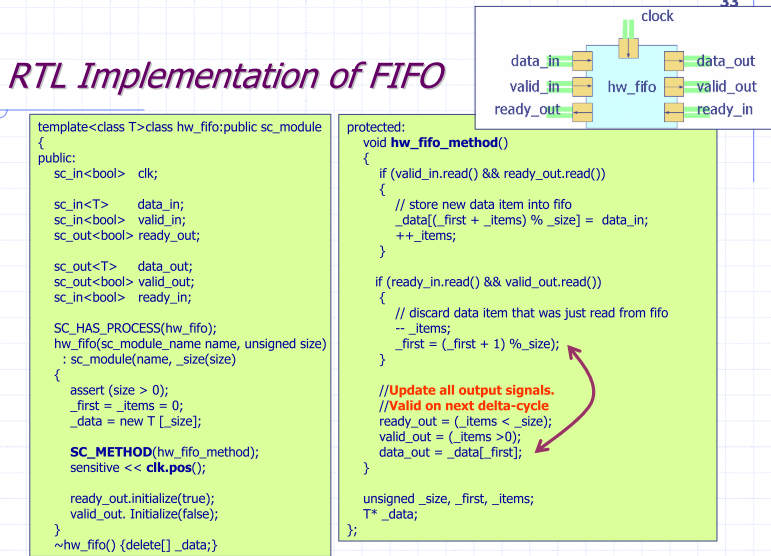
RTL Implementation of FIFO
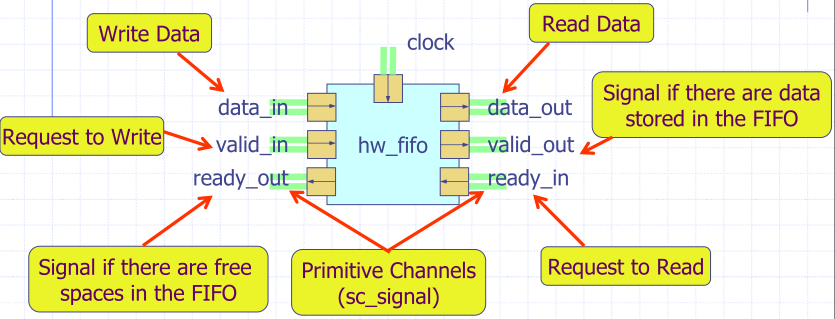
Definition of input/output.
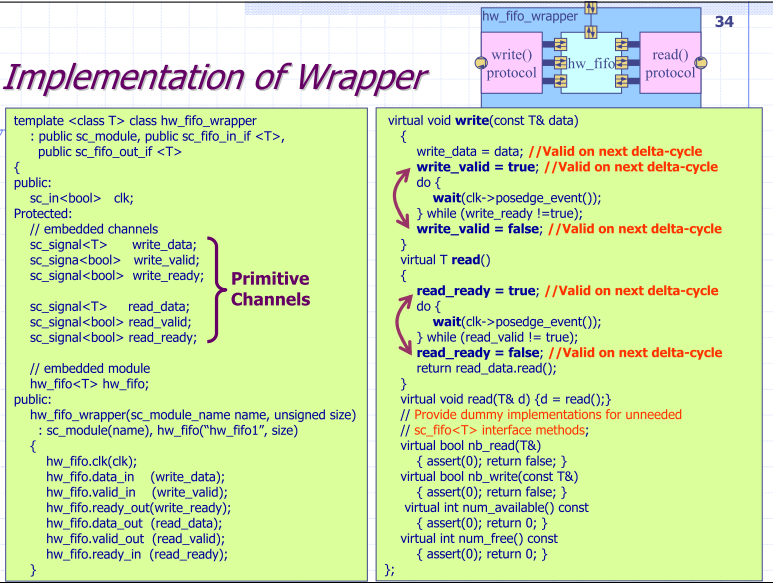
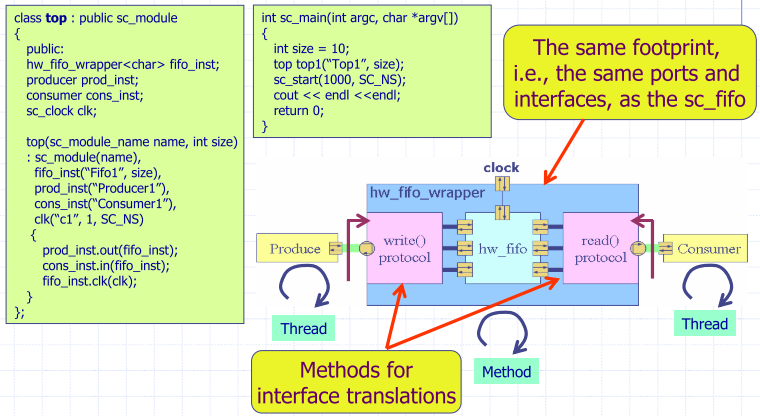
Implementation of Wrapper
Top Module with Hierarchical Channels
-
IOC5080(5940) System Model Design and Verification, Department of Computer Science, National Chiao-Tung University ↩