[Weekly Review] 2020/03/30-04/05
2020/03/30-04/05
This week, I began to learn the course UCB 61B, and finished the mid-report of my FYP. I also added some test of Cluster Group controller, as well as a new wrapper for Cluster Group, but had little progress of the FYP.
Next week, I hope I can finish the verification of the whole Cluster Group and return to the test of TileLink.
CS61B
Testing(Test-Driven Development, TDD)

Steps to developing according to TDD:
-
Identify a new feature.
-
Write a test for that feature.
-
Run the test. It should fail. (RED)
-
Write code that passes test. (GREEN)
-
- Implementation is certifiably good!
- Optional: Refactor code to make it faster, cleaner, etc.
And here is a Chinese blog which introduce more details.
TDD instructs developers to write new code only if an automated test has failed. This avoids duplication of code. The full form of TDD is Test-driven development.
Test-Driven development is a process of developing and running automated test before actual development of the application. Hence, TDD sometimes also called as Test First Development.
Some clarifications about TDD:
- TDD is neither about "Testing" nor about "Design".
- TDD does not mean "write some of the tests, then build a system that passes the tests.
- TDD does not mean "do lots of Testing."
In TDD more focus is on production code that verifies whether testing will work properly. In traditional testing, more focus is on test case design. Whether the test will show the proper/improper execution of the application in order to fulfill requirements.
In Agile Modeling (AM), you should "test with a purpose". You should know why you are testing something and what level its need to be tested.
TDD allows writing smaller code having single responsibility rather than monolithic procedures with multiple responsibilities. This makes the code simpler to understand.
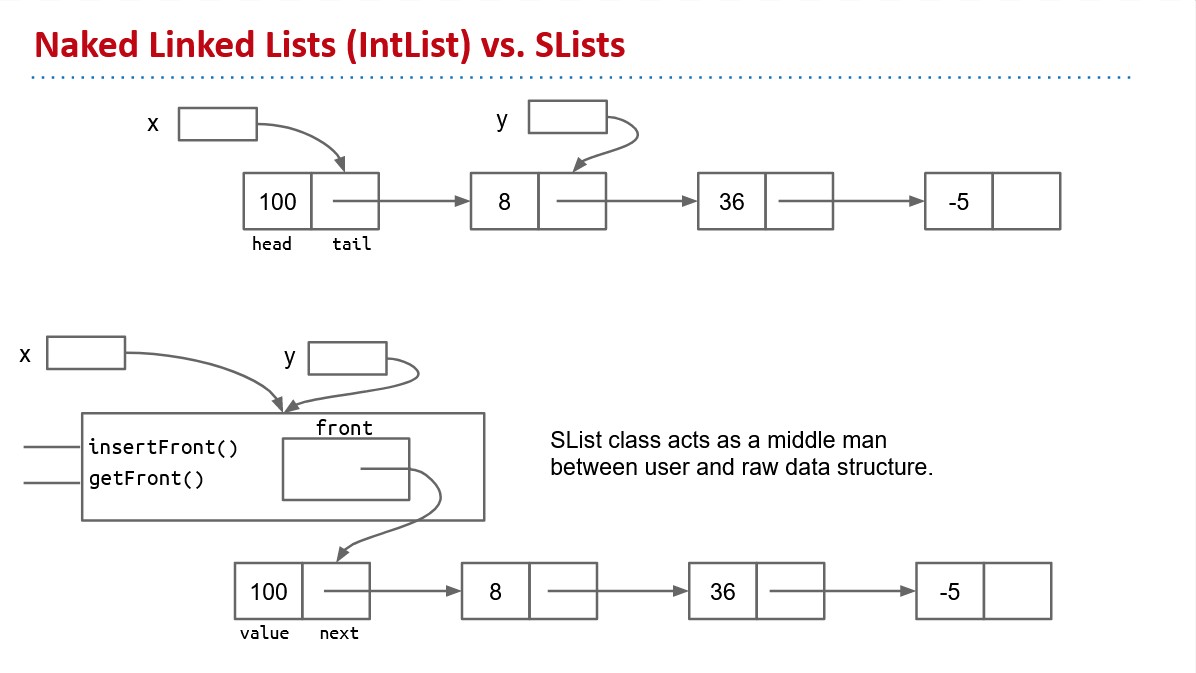
Naked Linked List(IntList) vs. SList
create a special node that is always there without
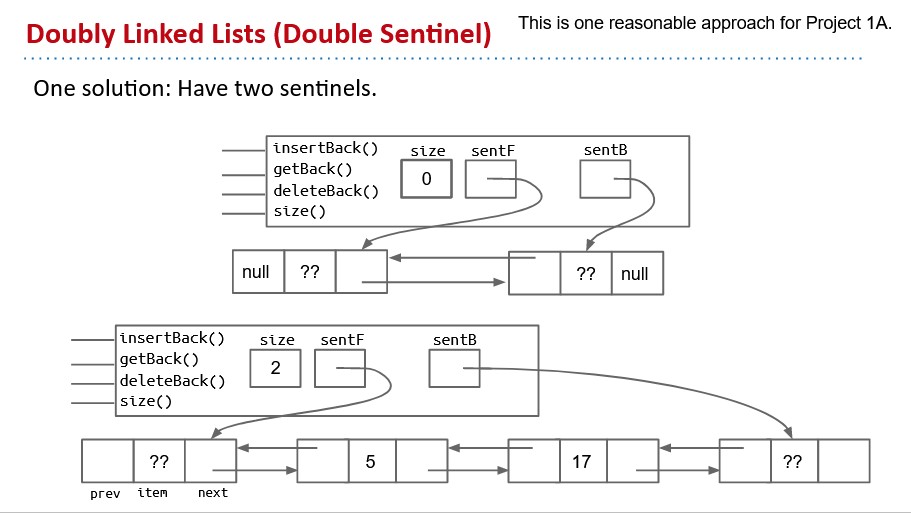
Doubly Linked List and Arrays
Add backwards links from every node
Non-obvious fact: This approach has an annoying special case: back sometimes points at the sentinel, and sometimes points at a ‘real’ node:
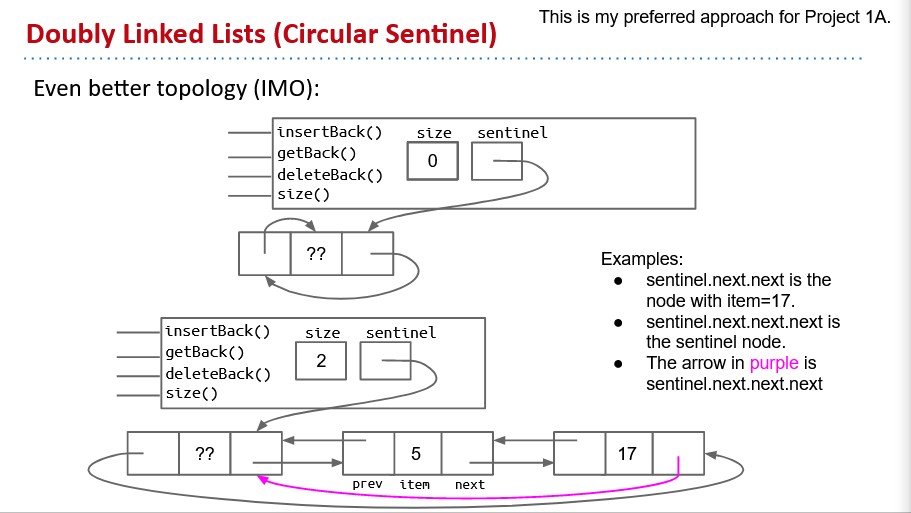
- Double sentinel
- Circular sentinel
Array
Arrays consist of:
-
A fixed integer length (cannot change!)
-
A sequence of N memory boxes where N=length, such that:
-
- All of the boxes hold the same type of value (and have same # of bits).
- The boxes are numbered 0 through length-1.
Arrays of Array Address
Arrays and Classes can both be used to organize a bunch of memory boxes.
- Array boxes are accessed using [] notation.
- Class boxes are accessed using dot notation.
- Array boxes must all be of the same type.
- Class boxes may be of different types.
- Array indices can be computed at runtime
Array Resizing
Use array copy.
public void addLast(int x) {
if (size == items.length) {
int[] a = new int[size + 1];
System.arraycopy(items, 0, a, 0, size);
items = a;
}
items[size] = x;
size += 1;
}
And it would be better if we separate this function into two:
private void resize(int capacity) {
int[] a = new int[capacity];
System.arraycopy(items, 0, a, 0, size);
items = a;
}
public void addLast(int x) {
if (size == items.length) {
resize(size + 1);
}
items[size] = x;
size += 1;
}
But if we want to insert say, 100,000 items, it will require 5,000,000,000 new containers.
public void addLast(int x) {
if (size == items.length) {
resize(size * RFACTOR);
}
items[size] = x;
size += 1;
}
So we can extends it more every time the array is full.
Array Memory Efficiency
An Array List should not only be efficient in time, but also efficient in space.
- Define the “usage ratio”
R = size / items.length; - Typical solution: Half array size when R < 0.25.
Sum: Four Different Approaches
/** Uses a basic for loop to sum A. */
public static int sum(int[] a) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i = i + 1) {
sum = sum + a[i];
}
return sum;
}
/** Uses enhanced for loop. */
public static int altSum(int[] a) {
int sum = 0;
for (int x : a) {
sum = sum + x;
}
return sum;
}
/** Uses recursion */
public static int altSum2(int[] a) {
return altSum2(a, 0);
}
/** Sums A starting from position k. */
private static int altSum2(int[] a, int k) {
if (k == a.length) {
return 0;
}
return a[k] + altSum2(a, k + 1);
}
/** Uses a basic for loop to sum A. */
public static int awfulSum(int[] a) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; sum += a[i], i++);
return sum;
}
Inheritance Subtype Polymorphism
Dynamic Method Selection
Suppose we call a method of an object using a variable with:
- compile-time type X
- run-time type Y Then if Y overrides the method, Y’s method is used instead.
- This is often known as “dynamic method selection”.
Encapsulation
A module is said to be encapsulated if its implementation is completely hidden, and it can be accessed only through a documented interface.
Inheritance Summary
how implements and extends can be used to enable interface inheritance and implementation inheritance.
- Interface inheritance: What (the class can do).
- Implementation inheritance: How (the class does it).
Interface Summary
Interfaces:
- Cannot be instantiated.
- Can provide either abstract or concrete methods.
- Use no keyword for abstract methods.
- Use default keyword for concrete methods.
- Can provide only public static final variables.
- Can provide only public methods.
Abstract Classes
Abstract classes are an intermediate level between interfaces and classes.
- Cannot be instantiated.
- Can provide either abstract or concrete methods.
- Use abstract keyword for abstract methods.
- Use no keyword for concrete methods.
- Can provide variables (any kind).
- Can provide methods (any kind).
abstract class GraphicObject {
int x, y;
...
void moveTo(int newX, int newY) {
...
}
abstract void draw();
abstract void resize();
}
class Circle extends GraphicObject {
void draw() {
...
}
void resize() {
...
}
}
class Rectangle extends GraphicObject {
void draw() {
...
}
void resize() {
...
}
}
Higher Order Functions (HoF)
Higher Order Function: A function that treats another function as data.
- e.g. takes a function as input.
Continuous Integration(CI)
Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice where developers integrate code into a shared repository frequently, preferably several times a day.1
One of the key benefits of integrating regularly is that you can detect errors quickly and locate them more easily. As each change introduced is typically small, pinpointing the specific change that introduced a defect can be done quickly.
In order to detect the errors, we need to write test cases firstly before we write the implementations.
BDD Behavior-driven development
https://tw.alphacamp.co/blog/bdd-tdd-cucumber-behaviour-driven-development
Chisel Syntax
ICR Not Available
When you see the error ICR not available on chisel-testers2 / firrtl master then you must haven't setSinkClock if you want to use expecyDequeieor setSourceClock if you want to use enqueue.
This error was defined at verilator backend by functions getSourceClocks and getSinkClocks.
Example usage is here.
test(new PassthroughQueue(UInt(8.W))) { c =>
c.in.initSource()
c.in.setSourceClock(c.clock)
c.out.initSink()
c.out.setSinkClock(c.clock)
fork {
c.in.enqueueSeq(Seq(42.U, 43.U, 44.U))
}.fork {
c.out.expectDequeueSeq(Seq(42.U, 43.U, 44.U))
}.join()
}
-
https://codeship.com/continuous-integration-essentials ↩