[Weekly Review] 2020/04/06-12
2020/04/06-12
This week, I re-began to learn data structure and algorithms. Also, knew the term retiming and its usage.
I also finished the verification of decoder, so only cluster group test and the Tilelink verifications left. Hope I can finish the framework of Tilelink test this week.
CS61B
Packages and Using Libraries
Environment Variables
Packages
To address the fact that classes might share names:
- A package is a namespace that organizes classes and interfaces.
- Naming convention: Package name starts with website address (backwards).
Generics, Conversion, Promotion
Immutable Data Types
An immutable data type is one for which an instance cannot change in any observable way after instantiation.
Advantage: Less to think about: Avoids bugs and makes debugging easier.
Disadvantage: Must create a new object anytime anything changes.
Exceptions, Access Control, Objects
Exceptions
Sometimes things go wrong. The Java approach to handling these exceptional events is to throw an exception.
Catch blocks can execute arbitrary code.
try {
d.receivePat();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Tried to pat: " + e);
d.eatTreat("banana");
}
Access Control
| Modifier | Class | Package | Subclass | World |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| public | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| protected | Y | Y | Y | N |
| private | Y | N | N | N |
Access Levels:
- Private declarations are parts of the implementation of a class that only that class needs.
- Package-private declarations are parts of the implementation of a package that other members of the package will need to complete the implementation.
- Protected declarations are things that subtypes might need, but subtype clients will not.
- Public declarations are declarations of the specification for the package, i.e. what clients of the package can rely on. Once deployed, these should not change.
Programming Efficiently
Efficiency comes in two flavors:
- Programming cost.
- How long does it take to develop your programs?
- How easy is it to read, modify, and maintain your code?
- More important than you might think!
- Majority of cost is in maintenance, not development!
- Execution cost (starting next week).
- How much time does your program take to execute?
- How much memory does your program require?
Some Java features discussed in 61B:
- Packages.
- Good: Keep code organized (in folders). Canonical names for classes and other things.
- Bad: More work to compile and run.
- Static type checking.
- Good: Speeds up runtime (no need to runtime type check). Catch errors early (before anybody runs the code).
- Bad: More verbose code.
- Inheritance (implementation and interface inheritance).
- Good: Interface inheritance allows subtype polymorphism. Implementation inheritance allows code reuse.
- Bad: Have to implement all features of an interface (can be many). Makes code harder to read/understand. More that we’ll discuss.
Asymptotic Analysis
Determine symbolic execution times.
Give statement counts or runtime in terms of input size.
- Good: Relates runtime to input sizes. Tells you how the algorithm scales.
- Bad: Doesn’t tell you about actual times.
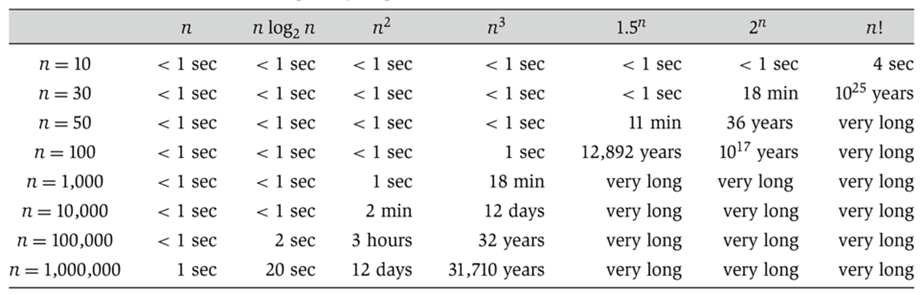
Intuitive Rules
- Ignore small inputs, e.g. treat 2N+1 just like 2N
- Ignore constant scaling factor, e.g. treat 2N, just like N.
Asymptotic Notation
Asymptotic notation (sometimes referred to as Bachmann-Landau notation) to describe order of growth.
| Informal meaning: | Family | Family Members | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Theta Θ(f(N)) | Order of growth is f(N). | Θ(N2) | N2/2 2N2 N2 + 38N + N |
| Big O O(f(N)) | Order of growth is less than or equal to f(N). | O(N2) | N2/2 2N2 lg(N) |
| Big Omega Ω(f(N)) | Order of growth is greater than or equal to f(N). | Ω(N2) | N2/2 2N2 eN |
| Tilde ~f(N) | Ratio converges to 1 for very large N. | ~2N2 | 2N2 2N2 + 5 |
1 + 2 + 3 + … + N = N(N+1)/2 = Θ(N2)
1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + … + N = 2N - 1 = Θ(N)
Recursion: C(N) = 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + … + 2N-1= 2N-1 = Θ(2N-1)
Binary Search: C(N) = 1 + 1 + … + 1 + 0 = k = ⌈lg N⌉ = Θ(log N)
The Merge Operation: C(N) = N * lg N = Θ(N * log N)
- Give half of the items away for sorting to one algorithm.
- Give the other half to some other algorithm.
- Merge the results: Θ(N) compares.
Amortized Analysis
Resizes to accommodate additional entries.
- When the array inside the ArrayList is full, double in size.
- Most add operations are constant time, but some are very expensive.
Given N items, cost of insert:
- Worst case: Θ(N)
- Average case: Θ(1) (unproven)
Empirical Analysis
Many possible sources of runtime strangeness:
- High system load
- Branch prediction
- Caching
- Just-in-time compilation (main suspect for Three Sum Bizarre)
- Large constants for low order terms: aN + N2 looks linear for large a.
Disjoint Sets
The Dynamic Connectivity Problem
public interface DisjointSets {
/** Connects two items P and Q. */
void connect(int p, int q);
/** Checks to see if two items are connected. */
boolean isConnected(int p, int q);
}
Rather than manually writing out every single connecting line, record the sets that something belongs to.
| Implementation | Constructor | connect | isConnected |
|---|---|---|---|
| QuickFindDS | Θ(N) | Θ(N) | Θ(1) |
| QuickUnionDS | Θ(N) | O(N) | O(N) |
| WeightedQuickUnionDS | Θ(N) | O(log N) | O(log N) |
QuickUnionDS : using a parent List to store the parents node value. Then when connecting two nodes, assign one's parents to another's parent.
WeightedQuickUnionDS: Modify quick-union to avoid tall trees.
- Track tree size (number of elements).
-
Always link root of smaller tree to larger tree.
- Use parent[] array as before, but also add size[] array.
- isConnected(int p, int q) requires no changes.
- connect(int p, int q) needs two changes:
- Link root of smaller tree to larger tree.
- Update size[] array.
The Zen of Python
- Beautiful is better than ugly.
- Explicit is better than implicit.
- Simple is better than complex.
- Complex is better than complicated.
- Flat is better than nested.
- Sparse is better than dense.
- Readability counts.
- Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
- Although practicality beats purity.
- Errors should never pass silently.
- Unless explicitly silenced.
- In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
- There should be one– and preferably only one –obvious way to do it.
- Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
- Now is better than never.
- Although never is often better than right now.
- If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
- If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
- Namespaces are one honking great idea – let's do more of those!
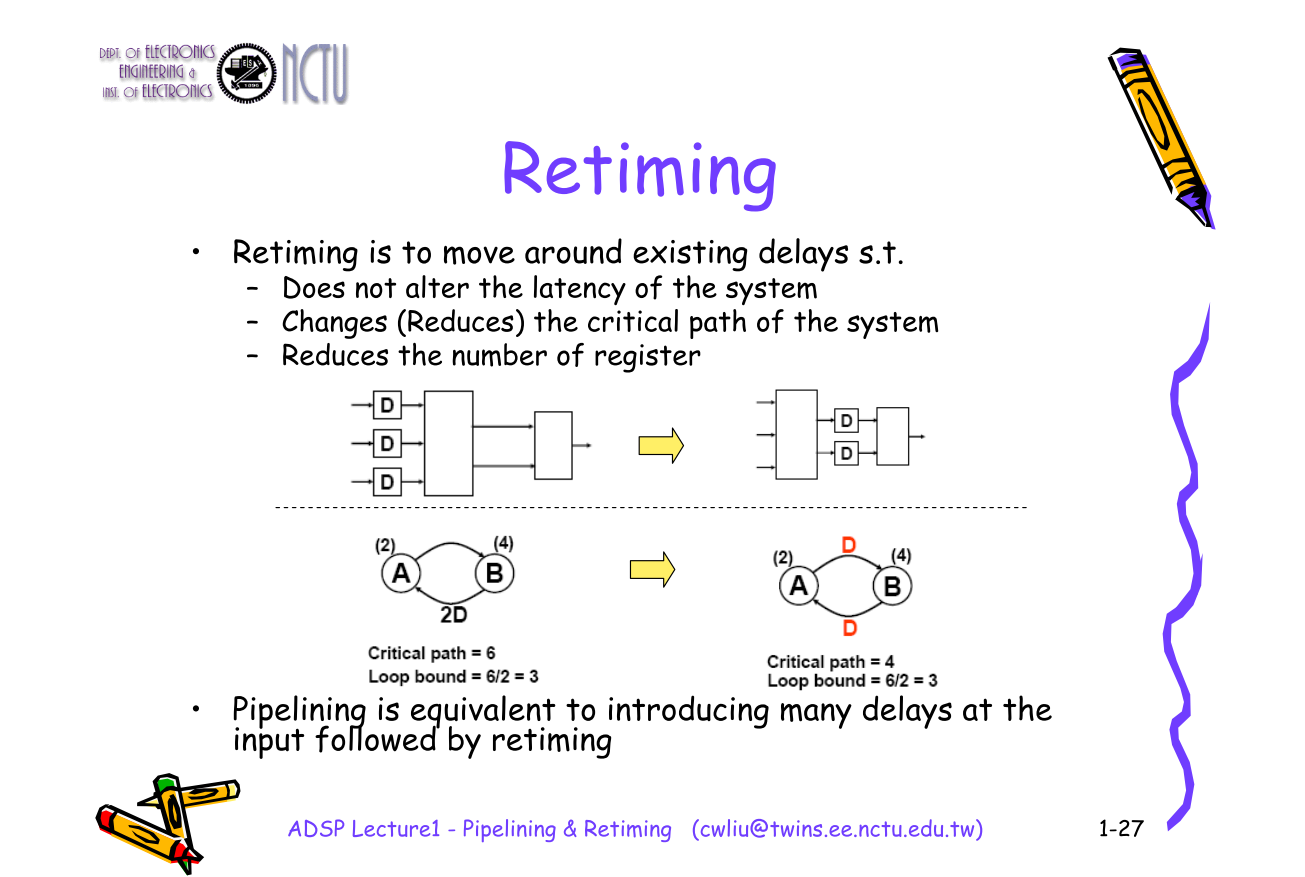
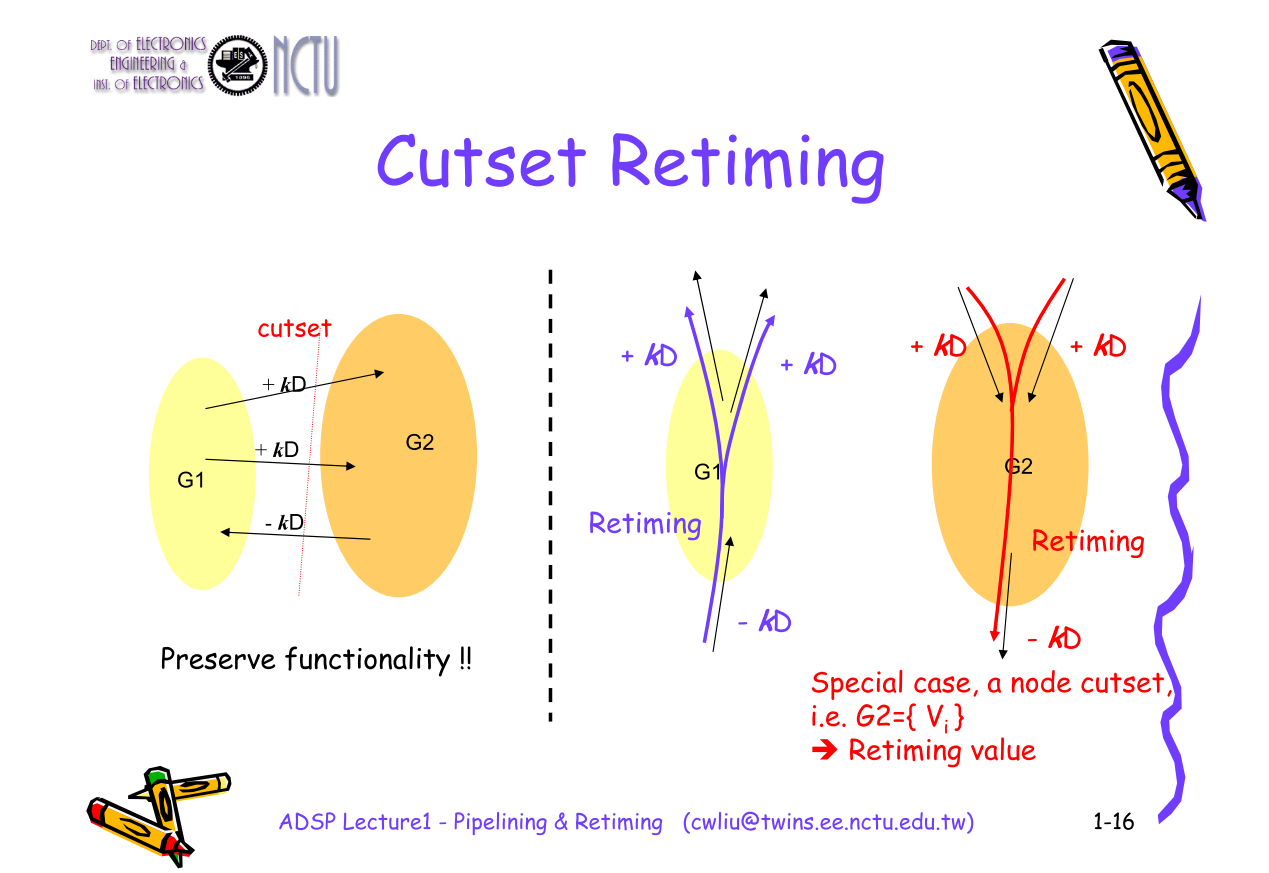
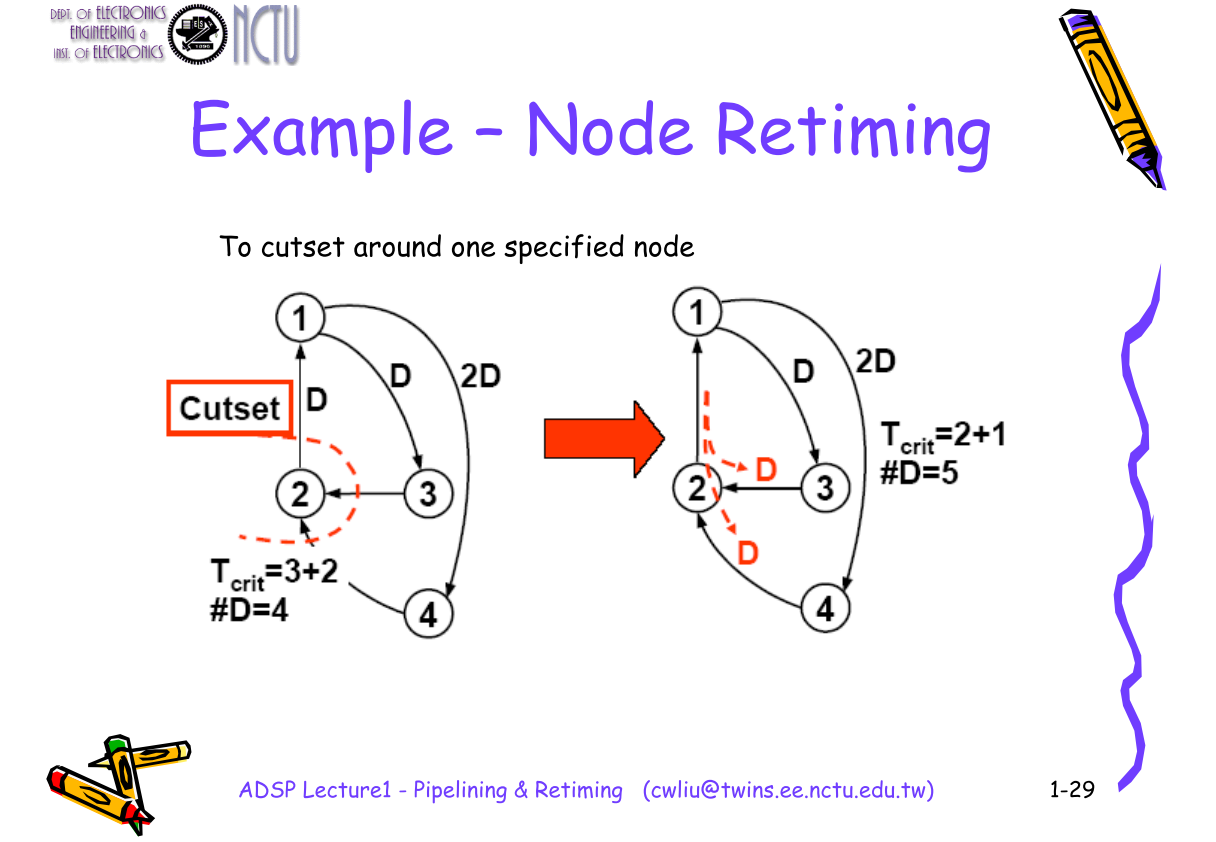
Cutset Retiming and Pipelining
Retiming is a powerful sequential circuit optimization technique for improving the performance of sequential circuits.
The concept of cuset retiming is the notion of moving storage devices across memoryless computational elements to improve the performance without changing the input-output latency.