[Emulate] Overview of SystemC Components
Overview of SystemC1
Overview of SystemC Components
Module and Hierarchy
SystemC separates the interface and implementation similar to VHDL. The C++ notion of header (.h file) is used for the entity and the notion of implementation (.cpp file) is used for the architecture.
Ports, Interfaces, and Channels
In SystemC, processes communicate using channels or events. Processes may also communicate across module boundaries. Modules may interconnect using channels, and connect via ports. The powerful ability to have interchangeable channels is implemented through a component called an
interface.
The provided channels include the synchronization primitives, and the communication channels, and others.
Interestingly, module interconnection happens programmatically in SystemC during the elaboration phase. This interconnection lets designers build regular structures using loops and conditional statements.
SystemC Simulation Kernel
The SystemC simulator has two major phases of operation: elaboration and execution. A third, often minor, phase occurs at the end of execution; this phase could be characterized as post-processing or cleanup.
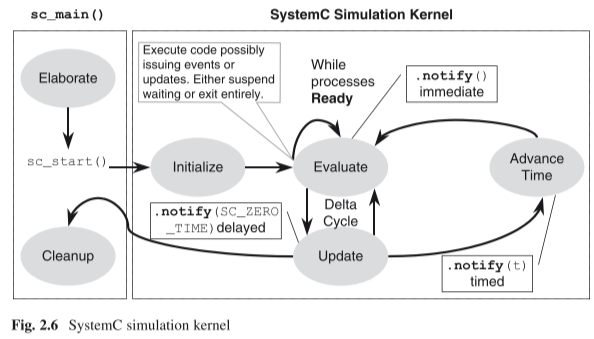
Execution of statements prior to the sc_start() function call are known as the elaboration phase. This phase is characterized by the initialization of data structures, the establishment of connectivity, and the preparation for the second phase, execution.
The execution phase hands control to the SystemC simulation kernel, which orchestrates the execution of processes to create an illusion of concurrency.
Finally, after returning from sc_start(), the post-processing stage begins. Post-processing is mostly optional. During post-processing, code may read data created during simulation and format reports or otherwise handle the results of simulation.
-
D. C. Black, J. Donovan, B. Bunton, and A. Keist, SystemC: From the Ground Up, Second Edition, 2nd ed. Springer US, 2010. ↩